Note
Click here to download the full example code
Audio Feature Extractions
Author: Moto Hira
torchaudio implements feature extractions commonly used in the audio
domain. They are available in torchaudio.functional and
torchaudio.transforms.
functional implements features as standalone functions.
They are stateless.
transforms implements features as objects,
using implementations from functional and torch.nn.Module.
They can be serialized using TorchScript.
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.functional as F
import torchaudio.transforms as T
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
1.13.0
0.13.0
Preparation
Note
When running this tutorial in Google Colab, install the required packages
!pip install librosa
from IPython.display import Audio
import librosa
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchaudio.utils import download_asset
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
SAMPLE_SPEECH = download_asset("tutorial-assets/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-src-sp0307-ch127535-sg0042.wav")
def plot_waveform(waveform, sr, title="Waveform"):
waveform = waveform.numpy()
num_channels, num_frames = waveform.shape
time_axis = torch.arange(0, num_frames) / sr
figure, axes = plt.subplots(num_channels, 1)
axes.plot(time_axis, waveform[0], linewidth=1)
axes.grid(True)
figure.suptitle(title)
plt.show(block=False)
def plot_spectrogram(specgram, title=None, ylabel="freq_bin"):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axs.set_title(title or "Spectrogram (db)")
axs.set_ylabel(ylabel)
axs.set_xlabel("frame")
im = axs.imshow(librosa.power_to_db(specgram), origin="lower", aspect="auto")
fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs)
plt.show(block=False)
def plot_fbank(fbank, title=None):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axs.set_title(title or "Filter bank")
axs.imshow(fbank, aspect="auto")
axs.set_ylabel("frequency bin")
axs.set_xlabel("mel bin")
plt.show(block=False)
Overview of audio features
The following diagram shows the relationship between common audio features and torchaudio APIs to generate them.
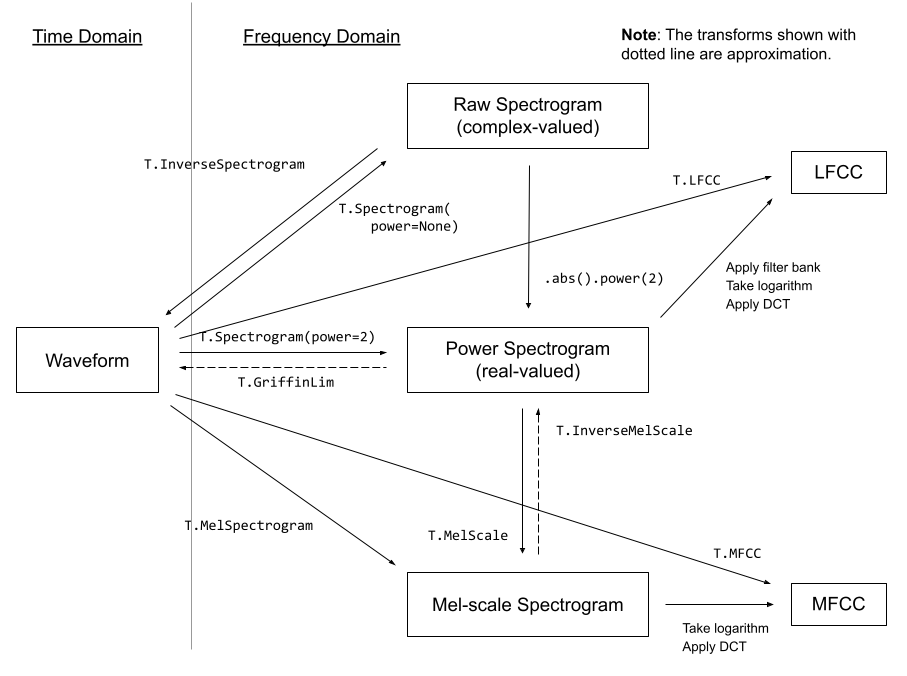
For the complete list of available features, please refer to the documentation.
Spectrogram
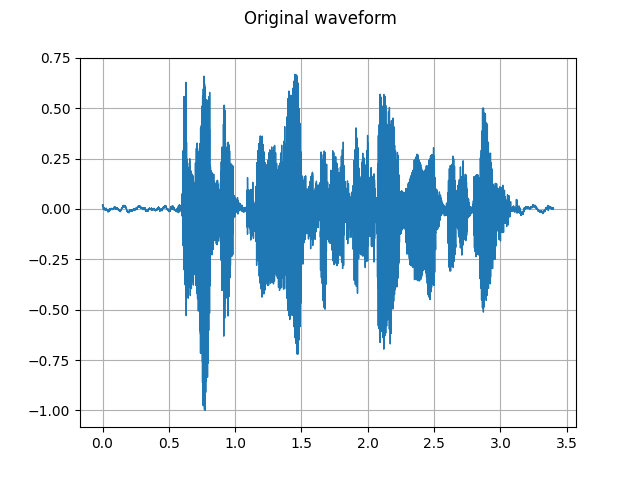
To get the frequency make-up of an audio signal as it varies with time,
you can use torchaudio.transforms.Spectrogram().
SPEECH_WAVEFORM, SAMPLE_RATE = torchaudio.load(SAMPLE_SPEECH)
plot_waveform(SPEECH_WAVEFORM, SAMPLE_RATE, title="Original waveform")
Audio(SPEECH_WAVEFORM.numpy(), rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
# Define transform
spectrogram = T.Spectrogram(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
center=True,
pad_mode="reflect",
power=2.0,
)
# Perform transform
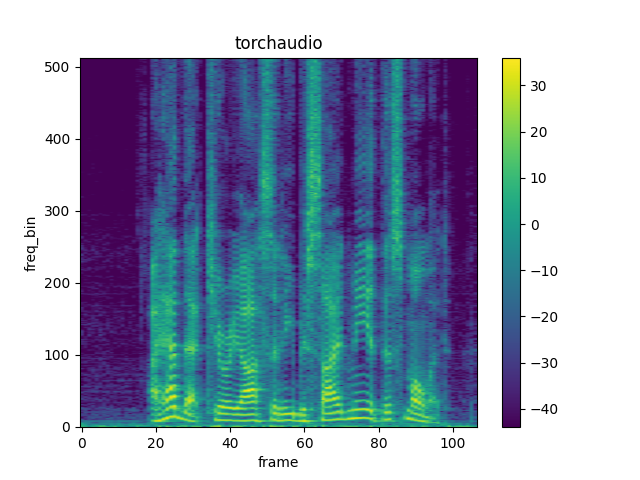
spec = spectrogram(SPEECH_WAVEFORM)
plot_spectrogram(spec[0], title="torchaudio")
GriffinLim
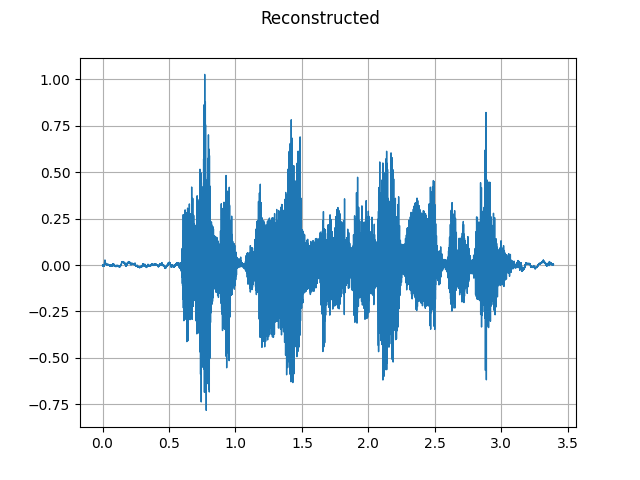
To recover a waveform from a spectrogram, you can use GriffinLim.
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
spec = T.Spectrogram(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
)(SPEECH_WAVEFORM)
griffin_lim = T.GriffinLim(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
)
reconstructed_waveform = griffin_lim(spec)
plot_waveform(reconstructed_waveform, SAMPLE_RATE, title="Reconstructed")
Audio(reconstructed_waveform, rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
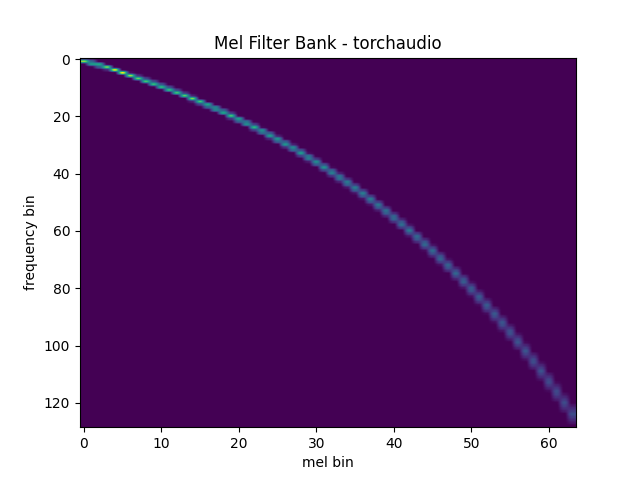
Mel Filter Bank
torchaudio.functional.melscale_fbanks() generates the filter bank
for converting frequency bins to mel-scale bins.
Since this function does not require input audio/features, there is no
equivalent transform in torchaudio.transforms().
n_fft = 256
n_mels = 64
sample_rate = 6000
mel_filters = F.melscale_fbanks(
int(n_fft // 2 + 1),
n_mels=n_mels,
f_min=0.0,
f_max=sample_rate / 2.0,
sample_rate=sample_rate,
norm="slaney",
)
plot_fbank(mel_filters, "Mel Filter Bank - torchaudio")
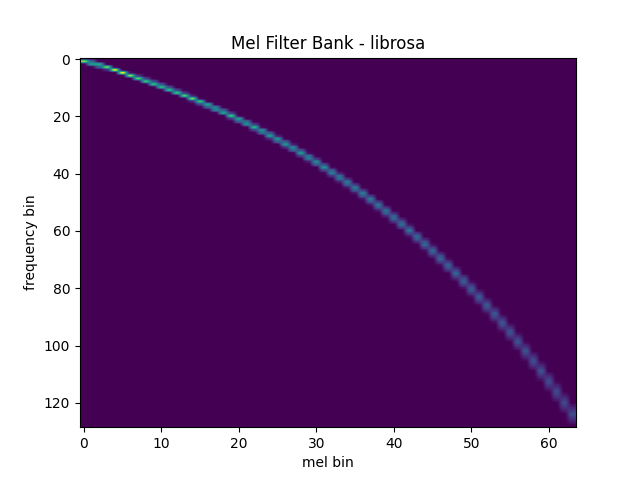
Comparison against librosa
For reference, here is the equivalent way to get the mel filter bank
with librosa.
mel_filters_librosa = librosa.filters.mel(
sr=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
n_mels=n_mels,
fmin=0.0,
fmax=sample_rate / 2.0,
norm="slaney",
htk=True,
).T
plot_fbank(mel_filters_librosa, "Mel Filter Bank - librosa")
mse = torch.square(mel_filters - mel_filters_librosa).mean().item()
print("Mean Square Difference: ", mse)
Mean Square Difference: 3.795462323290159e-17
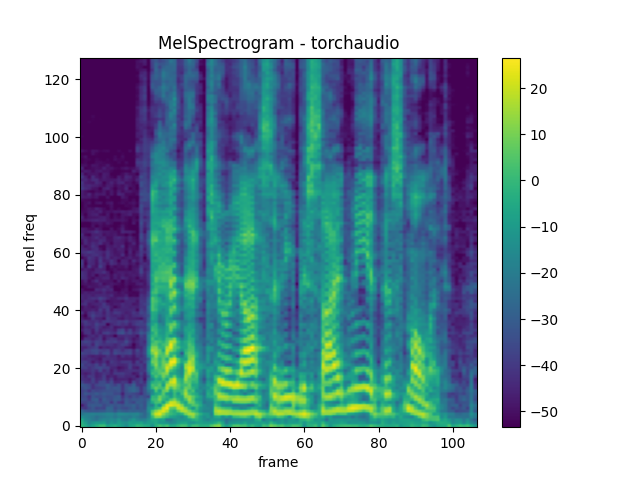
MelSpectrogram
Generating a mel-scale spectrogram involves generating a spectrogram
and performing mel-scale conversion. In torchaudio,
torchaudio.transforms.MelSpectrogram() provides
this functionality.
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
n_mels = 128
mel_spectrogram = T.MelSpectrogram(
sample_rate=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
center=True,
pad_mode="reflect",
power=2.0,
norm="slaney",
onesided=True,
n_mels=n_mels,
mel_scale="htk",
)
melspec = mel_spectrogram(SPEECH_WAVEFORM)
plot_spectrogram(melspec[0], title="MelSpectrogram - torchaudio", ylabel="mel freq")
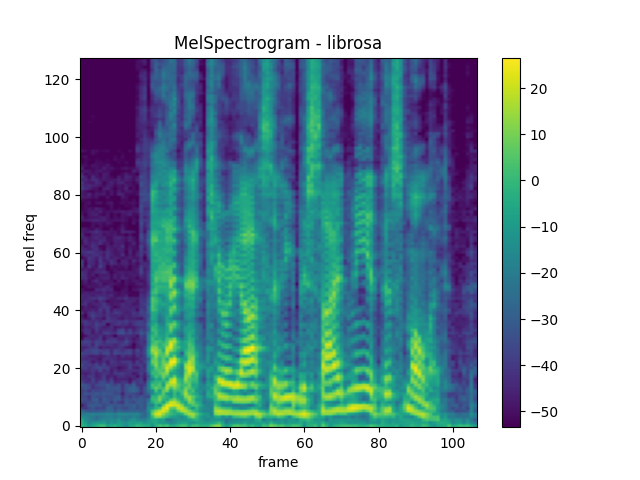
Comparison against librosa
For reference, here is the equivalent means of generating mel-scale
spectrograms with librosa.
melspec_librosa = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(
y=SPEECH_WAVEFORM.numpy()[0],
sr=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
hop_length=hop_length,
win_length=win_length,
center=True,
pad_mode="reflect",
power=2.0,
n_mels=n_mels,
norm="slaney",
htk=True,
)
plot_spectrogram(melspec_librosa, title="MelSpectrogram - librosa", ylabel="mel freq")
mse = torch.square(melspec - melspec_librosa).mean().item()
print("Mean Square Difference: ", mse)
Mean Square Difference: 1.0343034206883317e-09
MFCC
n_fft = 2048
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
n_mels = 256
n_mfcc = 256
mfcc_transform = T.MFCC(
sample_rate=sample_rate,
n_mfcc=n_mfcc,
melkwargs={
"n_fft": n_fft,
"n_mels": n_mels,
"hop_length": hop_length,
"mel_scale": "htk",
},
)
mfcc = mfcc_transform(SPEECH_WAVEFORM)
plot_spectrogram(mfcc[0])
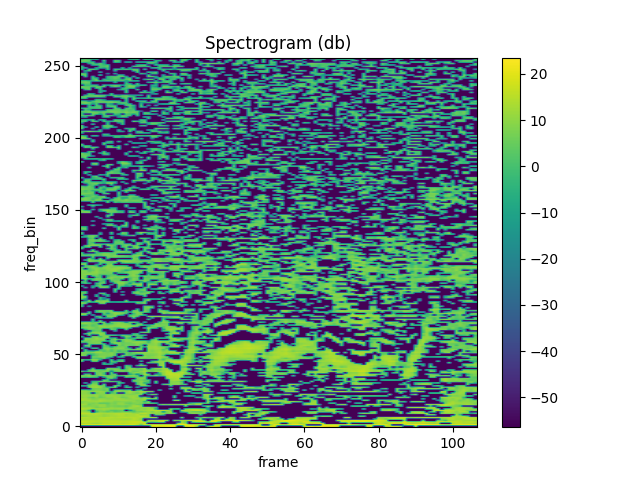
Comparison against librosa
melspec = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(
y=SPEECH_WAVEFORM.numpy()[0],
sr=sample_rate,
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
n_mels=n_mels,
htk=True,
norm=None,
)
mfcc_librosa = librosa.feature.mfcc(
S=librosa.core.spectrum.power_to_db(melspec),
n_mfcc=n_mfcc,
dct_type=2,
norm="ortho",
)
plot_spectrogram(mfcc_librosa)
mse = torch.square(mfcc - mfcc_librosa).mean().item()
print("Mean Square Difference: ", mse)
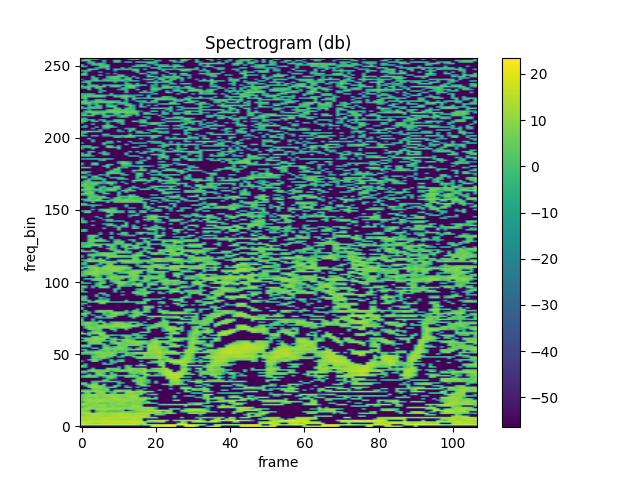
Mean Square Difference: 0.8103950023651123
LFCC
n_fft = 2048
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
n_lfcc = 256
lfcc_transform = T.LFCC(
sample_rate=sample_rate,
n_lfcc=n_lfcc,
speckwargs={
"n_fft": n_fft,
"win_length": win_length,
"hop_length": hop_length,
},
)
lfcc = lfcc_transform(SPEECH_WAVEFORM)
plot_spectrogram(lfcc[0])
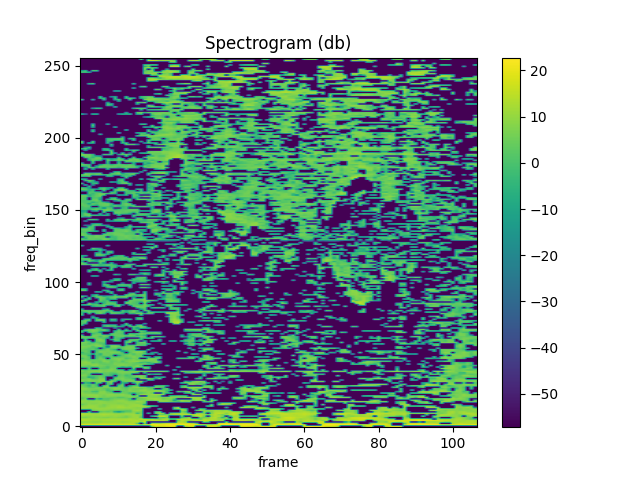
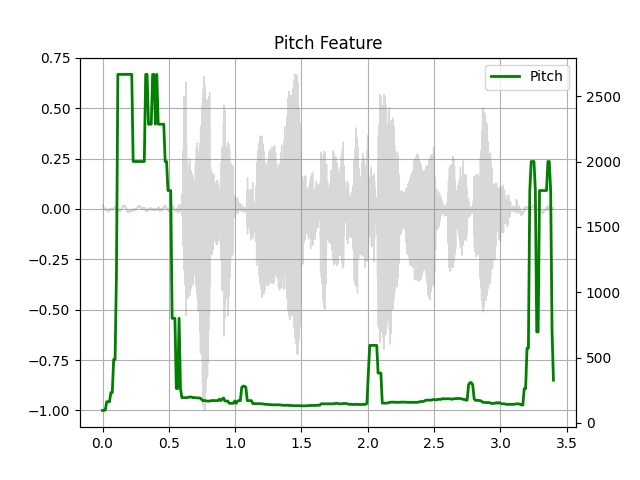
Pitch
pitch = F.detect_pitch_frequency(SPEECH_WAVEFORM, SAMPLE_RATE)
def plot_pitch(waveform, sr, pitch):
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axis.set_title("Pitch Feature")
axis.grid(True)
end_time = waveform.shape[1] / sr
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, waveform.shape[1])
axis.plot(time_axis, waveform[0], linewidth=1, color="gray", alpha=0.3)
axis2 = axis.twinx()
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, pitch.shape[1])
axis2.plot(time_axis, pitch[0], linewidth=2, label="Pitch", color="green")
axis2.legend(loc=0)
plt.show(block=False)
plot_pitch(SPEECH_WAVEFORM, SAMPLE_RATE, pitch)
Kaldi Pitch (beta)
Kaldi Pitch feature [1] is a pitch detection mechanism tuned for automatic
speech recognition (ASR) applications. This is a beta feature in torchaudio,
and it is available as torchaudio.functional.compute_kaldi_pitch().
A pitch extraction algorithm tuned for automatic speech recognition
Ghahremani, B. BabaAli, D. Povey, K. Riedhammer, J. Trmal and S. Khudanpur
2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, 2014, pp. 2494-2498, doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854049. [abstract], [paper]
pitch_feature = F.compute_kaldi_pitch(SPEECH_WAVEFORM, SAMPLE_RATE)
pitch, nfcc = pitch_feature[..., 0], pitch_feature[..., 1]
def plot_kaldi_pitch(waveform, sr, pitch, nfcc):
_, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axis.set_title("Kaldi Pitch Feature")
axis.grid(True)
end_time = waveform.shape[1] / sr
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, waveform.shape[1])
axis.plot(time_axis, waveform[0], linewidth=1, color="gray", alpha=0.3)
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, pitch.shape[1])
ln1 = axis.plot(time_axis, pitch[0], linewidth=2, label="Pitch", color="green")
axis.set_ylim((-1.3, 1.3))
axis2 = axis.twinx()
time_axis = torch.linspace(0, end_time, nfcc.shape[1])
ln2 = axis2.plot(time_axis, nfcc[0], linewidth=2, label="NFCC", color="blue", linestyle="--")
lns = ln1 + ln2
labels = [l.get_label() for l in lns]
axis.legend(lns, labels, loc=0)
plt.show(block=False)
plot_kaldi_pitch(SPEECH_WAVEFORM, SAMPLE_RATE, pitch, nfcc)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.581 seconds)



