Note
Click here to download the full example code
Device AV-ASR with Emformer RNN-T
Author: Pingchuan Ma, Moto Hira.
This tutorial shows how to run on-device audio-visual speech recognition (AV-ASR, or AVSR) with TorchAudio on a streaming device input, i.e. microphone on laptop. AV-ASR is the task of transcribing text from audio and visual streams, which has recently attracted a lot of research attention due to its robustness against noise.
Note
This tutorial requires ffmpeg, sentencepiece, mediapipe, opencv-python and scikit-image libraries.
There are multiple ways to install ffmpeg libraries.
If you are using Anaconda Python
distribution, conda install -c conda-forge 'ffmpeg<7' will
install compatible FFmpeg libraries.
You can run
pip install sentencepiece mediapipe opencv-python scikit-image to
install the other libraries mentioned.
Note
To run this tutorial, please make sure you are in the tutorial folder.
Note
We tested the tutorial on torchaudio version 2.0.2 on Macbook Pro (M1 Pro).
import numpy as np
import sentencepiece as spm
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchvision
Overview
The real-time AV-ASR system is presented as follows, which consists of three components, a data collection module, a pre-processing module and an end-to-end model. The data collection module is hardware, such as a microphone and camera. Its role is to collect information from the real world. Once the information is collected, the pre-processing module location and crop out face. Next, we feed the raw audio stream and the pre-processed video stream into our end-to-end model for inference.
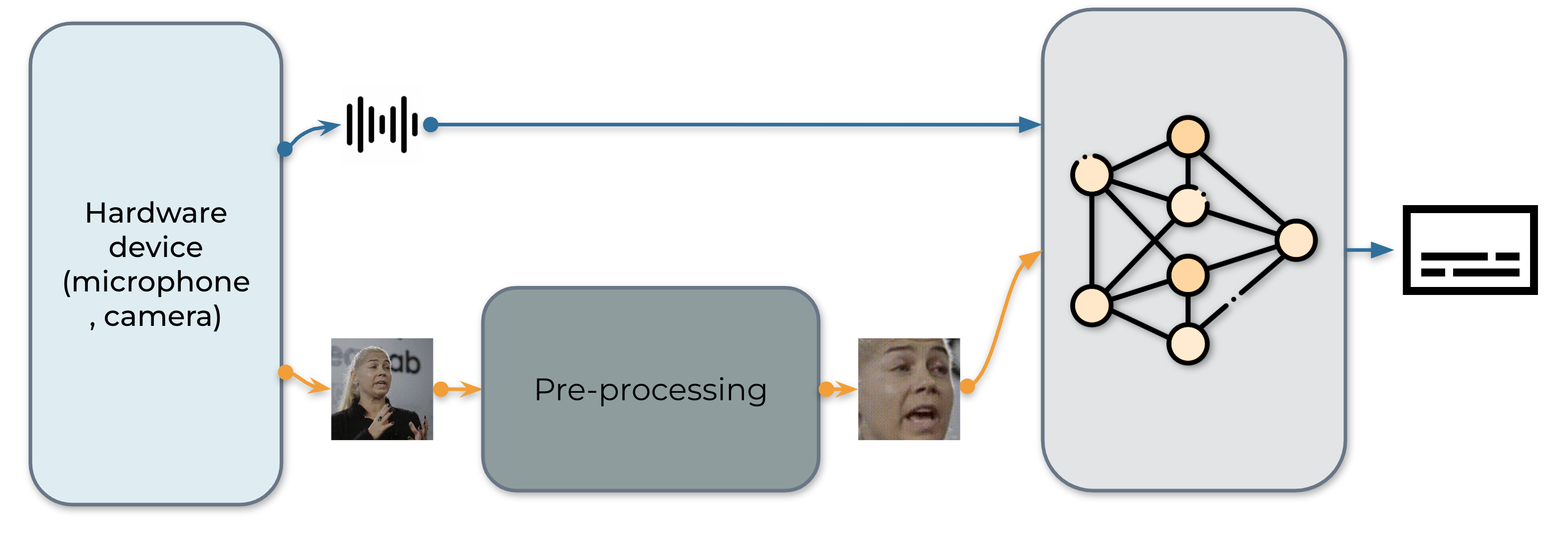
1. Data acquisition
Firstly, we define the function to collect videos from microphone and
camera. To be specific, we use StreamReader
class for the purpose of data collection, which supports capturing
audio/video from microphone and camera. For the detailed usage of this
class, please refer to the
tutorial.
def stream(q, format, option, src, segment_length, sample_rate):
print("Building StreamReader...")
streamer = torchaudio.io.StreamReader(src=src, format=format, option=option)
streamer.add_basic_video_stream(frames_per_chunk=segment_length, buffer_chunk_size=500, width=600, height=340)
streamer.add_basic_audio_stream(frames_per_chunk=segment_length * 640, sample_rate=sample_rate)
print(streamer.get_src_stream_info(0))
print(streamer.get_src_stream_info(1))
print("Streaming...")
print()
for (chunk_v, chunk_a) in streamer.stream(timeout=-1, backoff=1.0):
q.put([chunk_v, chunk_a])
class ContextCacher:
def __init__(self, segment_length: int, context_length: int, rate_ratio: int):
self.segment_length = segment_length
self.context_length = context_length
self.context_length_v = context_length
self.context_length_a = context_length * rate_ratio
self.context_v = torch.zeros([self.context_length_v, 3, 340, 600])
self.context_a = torch.zeros([self.context_length_a, 1])
def __call__(self, chunk_v, chunk_a):
if chunk_v.size(0) < self.segment_length:
chunk_v = torch.nn.functional.pad(chunk_v, (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, self.segment_length - chunk_v.size(0)))
if chunk_a.size(0) < self.segment_length * 640:
chunk_a = torch.nn.functional.pad(chunk_a, (0, 0, 0, self.segment_length * 640 - chunk_a.size(0)))
if self.context_length == 0:
return chunk_v.float(), chunk_a.float()
else:
chunk_with_context_v = torch.cat((self.context_v, chunk_v))
chunk_with_context_a = torch.cat((self.context_a, chunk_a))
self.context_v = chunk_v[-self.context_length_v :]
self.context_a = chunk_a[-self.context_length_a :]
return chunk_with_context_v.float(), chunk_with_context_a.float()
2. Pre-processing
Before feeding the raw stream into our model, each video sequence has to undergo a specific pre-processing procedure. This involves three critical steps. The first step is to perform face detection. Following that, each individual frame is aligned to a referenced frame, commonly known as the mean face, in order to normalize rotation and size differences across frames. The final step in the pre-processing module is to crop the face region from the aligned face image.

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, "../../examples")
from avsr.data_prep.detectors.mediapipe.detector import LandmarksDetector
from avsr.data_prep.detectors.mediapipe.video_process import VideoProcess
class FunctionalModule(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, functional):
super().__init__()
self.functional = functional
def forward(self, input):
return self.functional(input)
class Preprocessing(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.landmarks_detector = LandmarksDetector()
self.video_process = VideoProcess()
self.video_transform = torch.nn.Sequential(
FunctionalModule(
lambda n: [(lambda x: torchvision.transforms.functional.resize(x, 44, antialias=True))(i) for i in n]
),
FunctionalModule(lambda x: torch.stack(x)),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(0.0, 255.0),
torchvision.transforms.Grayscale(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(0.421, 0.165),
)
def forward(self, audio, video):
video = video.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).cpu().numpy().astype(np.uint8)
landmarks = self.landmarks_detector(video)
video = self.video_process(video, landmarks)
video = torch.tensor(video).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float()
video = self.video_transform(video)
audio = audio.mean(axis=-1, keepdim=True)
return audio, video
3. Building inference pipeline
The next step is to create components required for pipeline.
We use convolutional-based front-ends to extract features from both the raw audio and video streams. These features are then passed through a two-layer MLP for fusion. For our transducer model, we leverage the TorchAudio library, which incorporates an encoder (Emformer), a predictor, and a joint network. The architecture of the proposed AV-ASR model is illustrated as follows.
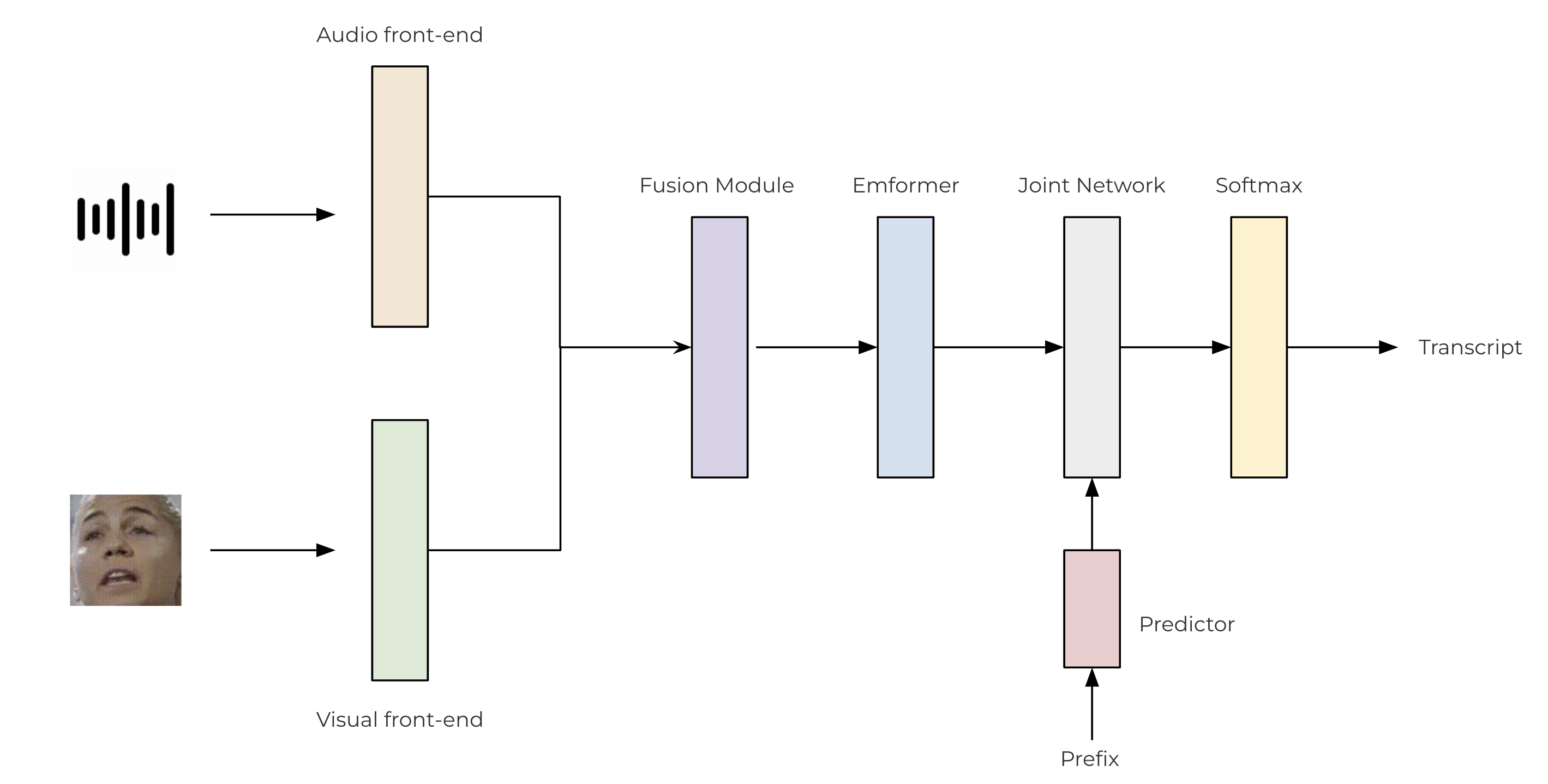
class SentencePieceTokenProcessor:
def __init__(self, sp_model):
self.sp_model = sp_model
self.post_process_remove_list = {
self.sp_model.unk_id(),
self.sp_model.eos_id(),
self.sp_model.pad_id(),
}
def __call__(self, tokens, lstrip: bool = True) -> str:
filtered_hypo_tokens = [
token_index for token_index in tokens[1:] if token_index not in self.post_process_remove_list
]
output_string = "".join(self.sp_model.id_to_piece(filtered_hypo_tokens)).replace("\u2581", " ")
if lstrip:
return output_string.lstrip()
else:
return output_string
class InferencePipeline(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, preprocessor, model, decoder, token_processor):
super().__init__()
self.preprocessor = preprocessor
self.model = model
self.decoder = decoder
self.token_processor = token_processor
self.state = None
self.hypotheses = None
def forward(self, audio, video):
audio, video = self.preprocessor(audio, video)
feats = self.model(audio.unsqueeze(0), video.unsqueeze(0))
length = torch.tensor([feats.size(1)], device=audio.device)
self.hypotheses, self.state = self.decoder.infer(feats, length, 10, state=self.state, hypothesis=self.hypotheses)
transcript = self.token_processor(self.hypotheses[0][0], lstrip=False)
return transcript
def _get_inference_pipeline(model_path, spm_model_path):
model = torch.jit.load(model_path)
model.eval()
sp_model = spm.SentencePieceProcessor(model_file=spm_model_path)
token_processor = SentencePieceTokenProcessor(sp_model)
decoder = torchaudio.models.RNNTBeamSearch(model.model, sp_model.get_piece_size())
return InferencePipeline(
preprocessor=Preprocessing(),
model=model,
decoder=decoder,
token_processor=token_processor,
)
4. The main process
The execution flow of the main process is as follows:
Initialize the inference pipeline.
Launch data acquisition subprocess.
Run inference.
Clean up
from torchaudio.utils import download_asset
def main(device, src, option=None):
print("Building pipeline...")
model_path = download_asset("tutorial-assets/device_avsr_model.pt")
spm_model_path = download_asset("tutorial-assets/spm_unigram_1023.model")
pipeline = _get_inference_pipeline(model_path, spm_model_path)
BUFFER_SIZE = 32
segment_length = 8
context_length = 4
sample_rate = 19200
frame_rate = 30
rate_ratio = sample_rate // frame_rate
cacher = ContextCacher(BUFFER_SIZE, context_length, rate_ratio)
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
ctx = mp.get_context("spawn")
@torch.inference_mode()
def infer():
num_video_frames = 0
video_chunks = []
audio_chunks = []
while True:
chunk_v, chunk_a = q.get()
num_video_frames += chunk_a.size(0) // 640
video_chunks.append(chunk_v)
audio_chunks.append(chunk_a)
if num_video_frames < BUFFER_SIZE:
continue
video = torch.cat(video_chunks)
audio = torch.cat(audio_chunks)
video, audio = cacher(video, audio)
pipeline.state, pipeline.hypotheses = None, None
transcript = pipeline(audio, video.float())
print(transcript, end="", flush=True)
num_video_frames = 0
video_chunks = []
audio_chunks = []
q = ctx.Queue()
p = ctx.Process(target=stream, args=(q, device, option, src, segment_length, sample_rate))
p.start()
infer()
p.join()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(
device="avfoundation",
src="0:1",
option={"framerate": "30", "pixel_format": "rgb24"},
)
Building pipeline...
Building StreamReader...
SourceVideoStream(media_type='video', codec='rawvideo', codec_long_name='raw video', format='uyvy422', bit_rate=0, num_frames=0, bits_per_sample=0, metadata={}, width=1552, height=1552, frame_rate=1000000.0)
SourceAudioStream(media_type='audio', codec='pcm_f32le', codec_long_name='PCM 32-bit floating point little-endian', format='flt', bit_rate=1536000, num_frames=0, bits_per_sample=0, metadata={}, sample_rate=48000.0, num_channels=1)
Streaming...
hello world
Tag: torchaudio.io
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.000 seconds)



