We are happy to announce the stable release, 1.0, for TorchRec and FBGEMM. TorchRec is the PyTorch native recommendation systems library, powered by FBGEMM’s (Facebook GEneral Matrix Multiplication) efficient, low-level kernels.
TorchRec
Initially open sourced in 2022, TorchRec provides common primitives for creating state-of-the-art personalization models:
- Simple, optimized APIs for distributed training across hundreds of GPUs
- Advanced sharding techniques for embeddings
- Modules common in authoring recommendation systems
- Frictionless path to distributed inference with APIs for quantization and sharding of TorchRec models
Since then, TorchRec has matured significantly, with wide internal adoption across many Meta production recommendation models for training and inference, alongside new features such as: variable batched embeddings, embedding offloading, zero collision hashing, etc. Furthermore, TorchRec has a presence outside of Meta, such as in recommendation models at Databricks and in the Twitter algorithm. As a result, standard TorchRec features have been marked as stable, with PyTorch style BC guarantees, and can be seen on the revamped TorchRec documentation.
FBGEMM
FBGEMM is a library that provides high-performance kernels for CPUs and GPUs. Since 2018, FBGEMM has supported the efficient execution of Meta-internal and external AI/ML workloads by expanding its scope from performance-critical kernels for inference on CPUs to more complex sparse operators for both training and inference – and recently for Generative AI – on CPUs and GPUs.
FBGEMM has been empowering TorchRec through its backend high-performance kernel implementations for recommendation workloads, ranging from embedding bag kernels to jagged tensor operations. Together with TorchRec, we released FBGEMM 1.0, which guarantees the functionality and backward-compatibility of several stable APIs serving its core features with enhanced documentation.
Performance
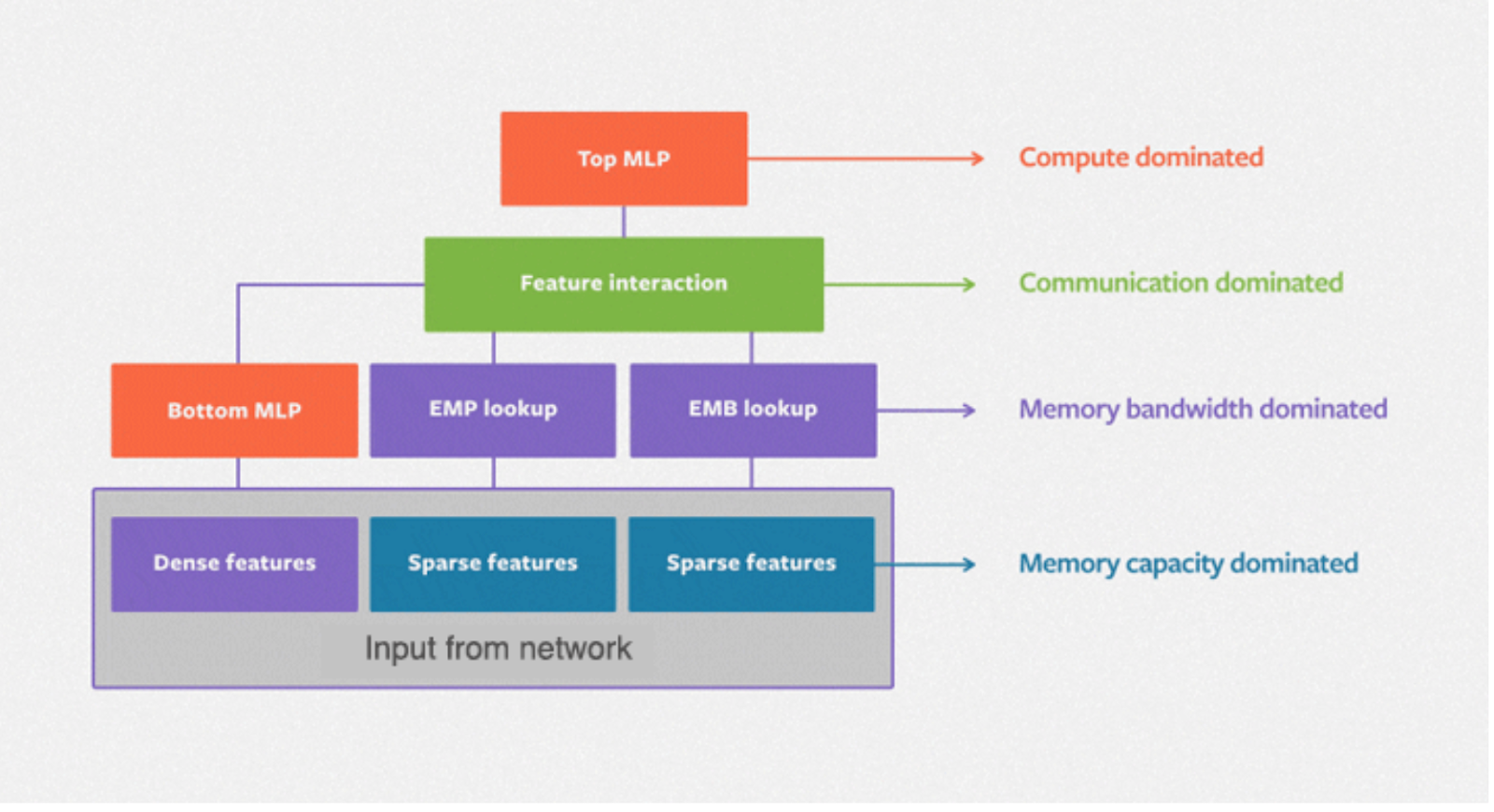
DLRM (Deep Learning Recommendation Model) is the standard neural network architecture for powering recommendations at Meta, with categorical features being processed through embeddings, while continuous (dense) features are processed with a bottom multilayer perceptron. The following diagram depicts the basic architecture of DLRM, with a second order interaction layer between the dense and sparse features and a top MLP for generating the prediction.
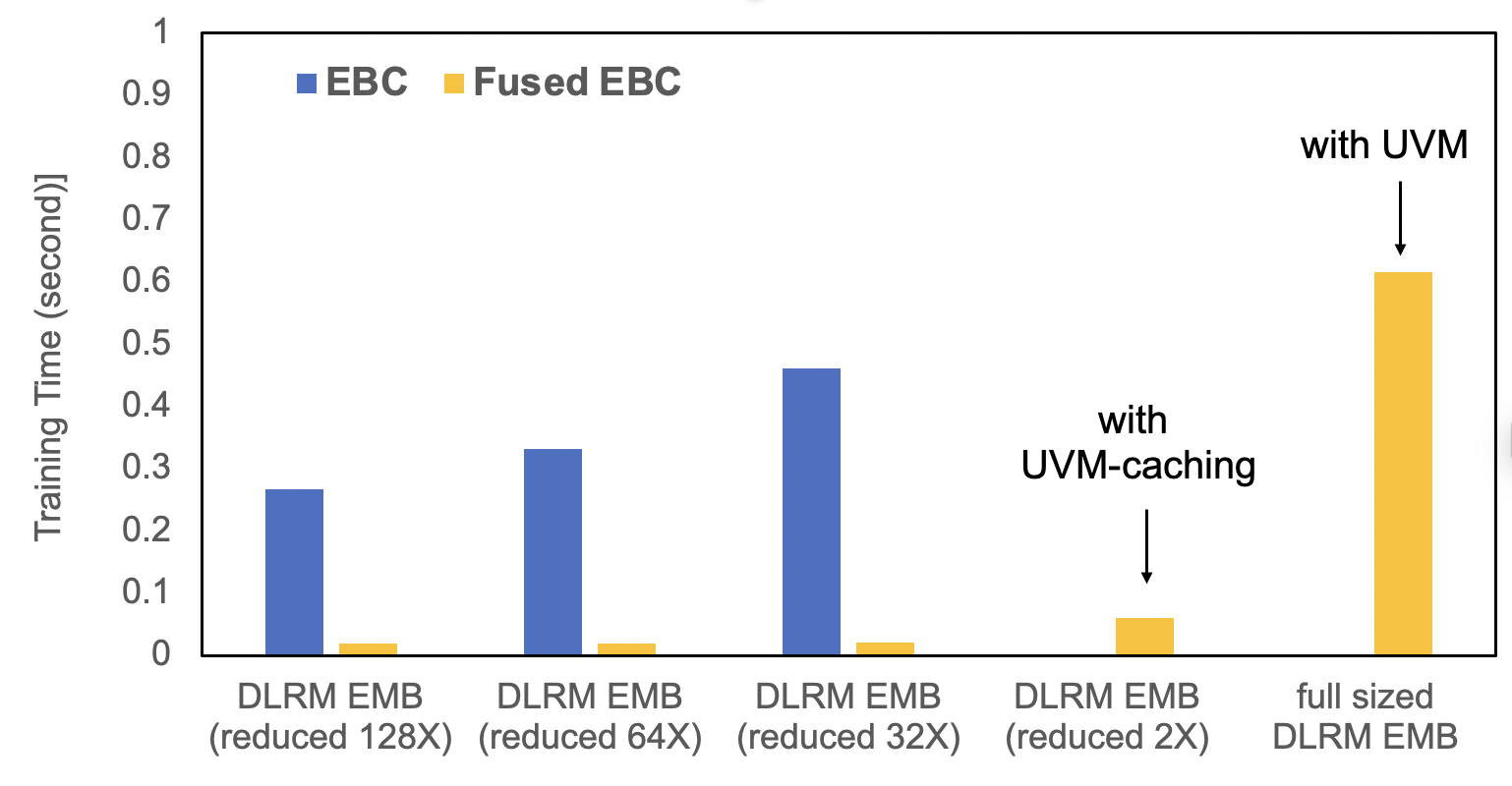
TorchRec provides standardized modules with significant optimizations in fusing embedding lookups. EBC is a traditional PyTorch embedding module implementation, containing a collection of torch.nn.EmbeddingBags. FusedEBC, powered by FBGEMM for high performance operations on embedding tables with a fused optimizer and UVM caching/management for alleviating memory constraints, is the optimized version present in sharded TorchRec modules for distributed training and inference. The below benchmark demonstrates the vast performance improvements of FusedEBC in comparison to a traditional PyTorch embedding module implementation (EBC) and the ability for FusedEBC to handle much larger embeddings than what is available on GPU memory with UVM caching.
TorchRec Data Types
TorchRec provides standard data types and modules for easy handling of distributed embeddings. Here is a simple example setting up a collection of embedding tables through TorchRec:
from torchrec import EmbeddingBagCollection
from torchrec import KeyedJaggedTensor
from torchrec import JaggedTensor
ebc = torchrec.EmbeddingBagCollection(
device="cpu",
tables=[
torchrec.EmbeddingBagConfig(
name="product_table",
embedding_dim=64,
num_embeddings=4096,
feature_names=["product"],
pooling=torchrec.PoolingType.SUM,
),
torchrec.EmbeddingBagConfig(
name="user_table",
embedding_dim=64,
num_embeddings=4096,
feature_names=["user"],
pooling=torchrec.PoolingType.SUM,
)
]
)
product_jt = JaggedTensor(
values=torch.tensor([1, 2, 1, 5]), lengths=torch.tensor([3, 1])
)
user_jt = JaggedTensor(values=torch.tensor([2, 3, 4, 1]), lengths=torch.tensor([2, 2]))
kjt = KeyedJaggedTensor.from_jt_dict({"product": product_jt, "user": user_jt})
print("Call EmbeddingBagCollection Forward: ", ebc(kjt))
Sharding
TorchRec provides a planner class that automatically generates an optimized sharding plan across many GPUs. Here we demonstrate generating a sharding plan across two GPUs:
from torchrec.distributed.planner import EmbeddingShardingPlanner, Topology
planner = EmbeddingShardingPlanner(
topology=Topology(
world_size=2,
compute_device="cuda",
)
)
plan = planner.collective_plan(ebc, [sharder], pg)
print(f"Sharding Plan generated: {plan}")
Model Parallel
TorchRec’s main distributed training API is DistributedModelParallel, which calls the planner to generate a sharding plan (demonstrated above) and shards TorchRec modules according to that plan. We demonstrate using DistributedModelParallel to our EmbeddingBagCollection for sharding embeddings distributed training:
model = torchrec.distributed.DistributedModelParallel(ebc, device=torch.device("cuda"))
Inference
TorchRec provides simple APIs for quantizing and sharding embeddings for a model for distributed inference. The usage is demonstrated below:
from torchrec.inference.modules import (
quantize_inference_model,
shard_quant_model,
)
quant_model = quantize_inference_model(ebc)
sharded_model, _ = shard_quant_model(
quant_model, compute_device=device, sharding_device=device
)
Conclusion
TorchRec and FBGEMM are now stable, with optimized features for large scale recommendation systems.
For setting up TorchRec and FBGEMM, check out the getting started guide.
We also recommend the comprehensive, end-to-end tutorial for introducing the features in TorchRec and FBGEMM.