Illustration of transforms¶
Note
Try on Colab or go to the end to download the full example code.
This example illustrates some of the various transforms available in the torchvision.transforms.v2 module.
from PIL import Image
from pathlib import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
from torchvision.transforms import v2
plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight'
# if you change the seed, make sure that the randomly-applied transforms
# properly show that the image can be both transformed and *not* transformed!
torch.manual_seed(0)
# If you're trying to run that on Colab, you can download the assets and the
# helpers from https://github.com/pytorch/vision/tree/main/gallery/
from helpers import plot
orig_img = Image.open(Path('../assets') / 'astronaut.jpg')
Geometric Transforms¶
Geometric image transformation refers to the process of altering the geometric properties of an image, such as its shape, size, orientation, or position. It involves applying mathematical operations to the image pixels or coordinates to achieve the desired transformation.
Pad¶
The Pad transform
(see also pad())
pads all image borders with some pixel values.
padded_imgs = [v2.Pad(padding=padding)(orig_img) for padding in (3, 10, 30, 50)]
plot([orig_img] + padded_imgs)

Resize¶
The Resize transform
(see also resize())
resizes an image.
resized_imgs = [v2.Resize(size=size)(orig_img) for size in (30, 50, 100, orig_img.size)]
plot([orig_img] + resized_imgs)

CenterCrop¶
The CenterCrop transform
(see also center_crop())
crops the given image at the center.
center_crops = [v2.CenterCrop(size=size)(orig_img) for size in (30, 50, 100, orig_img.size)]
plot([orig_img] + center_crops)

FiveCrop¶
The FiveCrop transform
(see also five_crop())
crops the given image into four corners and the central crop.
(top_left, top_right, bottom_left, bottom_right, center) = v2.FiveCrop(size=(100, 100))(orig_img)
plot([orig_img] + [top_left, top_right, bottom_left, bottom_right, center])

RandomPerspective¶
The RandomPerspective transform
(see also perspective())
performs random perspective transform on an image.
perspective_transformer = v2.RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.6, p=1.0)
perspective_imgs = [perspective_transformer(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + perspective_imgs)

RandomRotation¶
The RandomRotation transform
(see also rotate())
rotates an image with random angle.
rotater = v2.RandomRotation(degrees=(0, 180))
rotated_imgs = [rotater(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + rotated_imgs)

RandomAffine¶
The RandomAffine transform
(see also affine())
performs random affine transform on an image.
affine_transfomer = v2.RandomAffine(degrees=(30, 70), translate=(0.1, 0.3), scale=(0.5, 0.75))
affine_imgs = [affine_transfomer(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + affine_imgs)

ElasticTransform¶
The ElasticTransform transform
(see also elastic_transform())
Randomly transforms the morphology of objects in images and produces a
see-through-water-like effect.
elastic_transformer = v2.ElasticTransform(alpha=250.0)
transformed_imgs = [elastic_transformer(orig_img) for _ in range(2)]
plot([orig_img] + transformed_imgs)

RandomCrop¶
The RandomCrop transform
(see also crop())
crops an image at a random location.
cropper = v2.RandomCrop(size=(128, 128))
crops = [cropper(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + crops)

RandomResizedCrop¶
The RandomResizedCrop transform
(see also resized_crop())
crops an image at a random location, and then resizes the crop to a given
size.
resize_cropper = v2.RandomResizedCrop(size=(32, 32))
resized_crops = [resize_cropper(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + resized_crops)

Photometric Transforms¶
Photometric image transformation refers to the process of modifying the photometric properties of an image, such as its brightness, contrast, color, or tone. These transformations are applied to change the visual appearance of an image while preserving its geometric structure.
Except Grayscale, the following transforms are random,
which means that the same transform
instance will produce different result each time it transforms a given image.
Grayscale¶
The Grayscale transform
(see also to_grayscale())
converts an image to grayscale
gray_img = v2.Grayscale()(orig_img)
plot([orig_img, gray_img], cmap='gray')

ColorJitter¶
The ColorJitter transform
randomly changes the brightness, contrast, saturation, hue, and other properties of an image.
jitter = v2.ColorJitter(brightness=.5, hue=.3)
jittered_imgs = [jitter(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + jittered_imgs)

GaussianBlur¶
The GaussianBlur transform
(see also gaussian_blur())
performs gaussian blur transform on an image.
blurrer = v2.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=(5, 9), sigma=(0.1, 5.))
blurred_imgs = [blurrer(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + blurred_imgs)

RandomInvert¶
The RandomInvert transform
(see also invert())
randomly inverts the colors of the given image.
inverter = v2.RandomInvert()
invertered_imgs = [inverter(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + invertered_imgs)

RandomPosterize¶
The RandomPosterize transform
(see also posterize())
randomly posterizes the image by reducing the number of bits
of each color channel.
posterizer = v2.RandomPosterize(bits=2)
posterized_imgs = [posterizer(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + posterized_imgs)

RandomSolarize¶
The RandomSolarize transform
(see also solarize())
randomly solarizes the image by inverting all pixel values above
the threshold.
solarizer = v2.RandomSolarize(threshold=192.0)
solarized_imgs = [solarizer(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + solarized_imgs)

RandomAdjustSharpness¶
The RandomAdjustSharpness transform
(see also adjust_sharpness())
randomly adjusts the sharpness of the given image.
sharpness_adjuster = v2.RandomAdjustSharpness(sharpness_factor=2)
sharpened_imgs = [sharpness_adjuster(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + sharpened_imgs)

RandomAutocontrast¶
The RandomAutocontrast transform
(see also autocontrast())
randomly applies autocontrast to the given image.
autocontraster = v2.RandomAutocontrast()
autocontrasted_imgs = [autocontraster(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + autocontrasted_imgs)

RandomEqualize¶
The RandomEqualize transform
(see also equalize())
randomly equalizes the histogram of the given image.
equalizer = v2.RandomEqualize()
equalized_imgs = [equalizer(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + equalized_imgs)

JPEG¶
The JPEG transform
(see also jpeg())
applies JPEG compression to the given image with random
degree of compression.

Augmentation Transforms¶
The following transforms are combinations of multiple transforms, either geometric or photometric, or both.
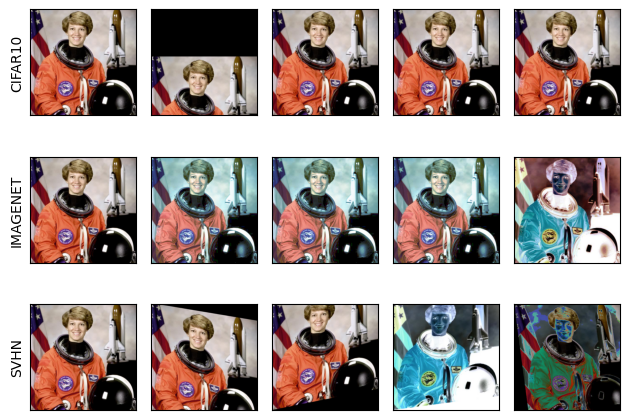
AutoAugment¶
The AutoAugment transform
automatically augments data based on a given auto-augmentation policy.
See AutoAugmentPolicy for the available policies.
policies = [v2.AutoAugmentPolicy.CIFAR10, v2.AutoAugmentPolicy.IMAGENET, v2.AutoAugmentPolicy.SVHN]
augmenters = [v2.AutoAugment(policy) for policy in policies]
imgs = [
[augmenter(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
for augmenter in augmenters
]
row_title = [str(policy).split('.')[-1] for policy in policies]
plot([[orig_img] + row for row in imgs], row_title=row_title)
RandAugment¶
The RandAugment is an alternate version of AutoAugment.
augmenter = v2.RandAugment()
imgs = [augmenter(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + imgs)

TrivialAugmentWide¶
The TrivialAugmentWide is an alternate implementation of AutoAugment.
However, instead of transforming an image multiple times, it transforms an image only once
using a random transform from a given list with a random strength number.
augmenter = v2.TrivialAugmentWide()
imgs = [augmenter(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + imgs)

AugMix¶
The AugMix transform interpolates between augmented versions of an image.

Randomly-applied Transforms¶
The following transforms are randomly-applied given a probability p. That is, given p = 0.5,
there is a 50% chance to return the original image, and a 50% chance to return the transformed image,
even when called with the same transform instance!
RandomHorizontalFlip¶
The RandomHorizontalFlip transform
(see also hflip())
performs horizontal flip of an image, with a given probability.
hflipper = v2.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5)
transformed_imgs = [hflipper(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + transformed_imgs)

RandomVerticalFlip¶
The RandomVerticalFlip transform
(see also vflip())
performs vertical flip of an image, with a given probability.
vflipper = v2.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.5)
transformed_imgs = [vflipper(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + transformed_imgs)

RandomApply¶
The RandomApply transform
randomly applies a list of transforms, with a given probability.
applier = v2.RandomApply(transforms=[v2.RandomCrop(size=(64, 64))], p=0.5)
transformed_imgs = [applier(orig_img) for _ in range(4)]
plot([orig_img] + transformed_imgs)

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.913 seconds)
