As part of this blog series, we share updates on new projects joining the PyTorch Ecosystem and highlight projects currently under consideration that may benefit from broader community engagement.
Ecosystem Project Spotlights
We’re happy to welcome several projects to the PyTorch Ecosystem since our last update. Here’s a short intro to our newest PyTorch Ecosystem projects.
Ecosystem projects.
FlagGems
Built on the Triton language, FlagGems is a plugin-based PyTorch operator and kernel library designed to democratize AI compute. Its mission: to enable a write-once, JIT-everywhere experience, so developers can deploy optimized kernels effortlessly across a wide spectrum of hardware backends. FlagGems recently joined the PyTorch Ecosystem upon acceptance by the PyTorch Ecosystem Working Group. With over 180 operators already implemented—spanning native PyTorch ops and widely used custom ops for large models—FlagGems is evolving fast to keep pace with the generative AI frontier.
Read more about FlagGems joining the PyTorch Ecosystem.
Kubeflow Trainer
Kubeflow Trainer is a Kubernetes-native project enabling scalable, distributed training of AI models and purpose-built for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs). It simplifies the scale-out of training workloads on multiple nodes, managing large datasets efficiently and ensuring fault-tolerance. Kubeflow Trainer project has been recently integrated into the PyTorch ecosystem, ensuring that Kubeflow Trainer aligns with PyTorch’s standards and practices to give developers a reliable, scalable, and community-backed solution to run PyTorch on Kubernetes. Kubeflow Trainer democratizes AI model training on Kubernetes and significantly improves the development experience for AI practitioners.
Read more about Kubeflow Trainer joining the PyTorch Ecosystem.
LMCache
LMCache is an LLM serving engine extension that combines with vLLM or SGLang to reduce TTFT and increase throughput, especially under long-context scenarios. By storing the KV caches of reusable texts across various locations, including (GPU, CPU DRAM, Local Disk, Databases), LMCache reuses the KV caches of any reused text (not necessarily prefix) in any serving engine instance. Thus, LMCache saves precious GPU cycles and reduces user response delay.
under long-context scenarios. By storing the KV caches of reusable texts across various locations, including (GPU, CPU DRAM, Local Disk, Databases), LMCache reuses the KV caches of any reused text (not necessarily prefix) in any serving engine instance. Thus, LMCache saves precious GPU cycles and reduces user response delay.
By combining LMCache with vLLM, developers achieve 3-10x delay savings and GPU cycle reduction in many LLM use cases, including multi-round QA and RAG.
Read more about LMCache joining the PyTorch Ecosystem.
DeepInverse
DeepInverse is an open-source PyTorch-based library for imaging inverse problems. DeepInverse implements all steps for image reconstruction, including efficient forward operators, defining and solving variational problems and designing and training advanced neural networks, for a wide set of domains (medical imaging, astronomical imaging, remote sensing, computational photography, compressed sensing and more).
reconstruction, including efficient forward operators, defining and solving variational problems and designing and training advanced neural networks, for a wide set of domains (medical imaging, astronomical imaging, remote sensing, computational photography, compressed sensing and more).
Read more about DeepInverse joining the PyTorch Ecosystem.
Feast
Feast (Feature Store) is an open-source feature store that helps teams operate production ML systems at scale by allowing them to define,manage, validate, and serve features for production AI/ML.
Feast’s feature store is composed of two foundational components: (1) an offline store for historical feature extraction used in model training and an (2) online store for serving features at low-latency in production systems and applications. Feast is a configurable operational data system that re-uses existing infrastructure to manage and serve machine learning features to realtime models.
NeuralOperator
NeuralOperator is a comprehensive library for learning neural operators in PyTorch. It is the official implementation for Fourier Neural Operators and Tensorized Neural Operators. Unlike regular neural networks, neural operators enable learning mapping between function spaces, and this library provides all of the tools to do so on your own data. Neural operators are also resolution invariant, so your trained operator can be applied on data of any resolution.
Read more about NeuralOperator joining the PyTorch Ecosystem.
PINA
PINA is an open source library designed to simplify and accelerate the development of Scientific Machine Learning (SciML) solutions. It provides a consistent and modular framework for building and experimenting with models such as Neural Networks, Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs), Neural Operators and more. Designed with composable abstractions, PINA allows researchers to plug in, replace, or extend components effortlessly, making experimentation both fast and flexible. It scales seamlessly across devices, delivering performance close to hand-crafted implementations while remaining easy to use.
Read more about PINA joining the PyTorch Ecosystem.
verl
verl is a flexible, efficient and production-ready RL training library for large language models (LLMs). verl is flexible and research-friendly: the hybrid-controller programming model enables flexible representation of complex post-training dataflows, expressing algorithms such as GRPO, PPO in a few lines of code; it provides reproducible state-of-the-art RL recipes for LLM reasoning models such as DAPO; and it is seamlessly integrated with existing LLM libraries such as FSDP2, Megatron-LM, vLLM, SGLang, transformers, etc.

verl is fast and production-ready: the flexible device mapping supports various placements of models onto different sets of GPUs for efficient resource utilization and scalability across different cluster sizes; the 3D-HybridEngine eliminates memory redundancy and reduces communication overhead during transitions between training and rollout phases; and asynchronous rollout with tool calling optimizations boosts end-to-end training throughput significantly.
Up and Coming Project Spotlight
As part of this series, we highlight projects under consideration for the PyTorch Ecosystem and that we believe will benefit from more eyes and contributors. This time it’s sc2bench’s turn.
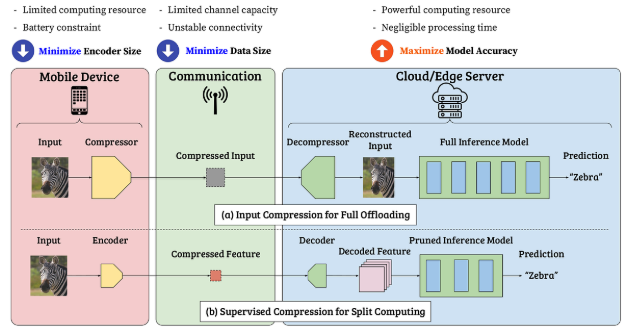
sc2bench
sc2bench is a Python package built on PyTorch and torchdistill (PyTorch Ecosystem) for facilitating research on supervised compression for split computing (SC2).
Benefits of using sc2bench
- A unified framework
sc2bench is carefully designed to integrate diverse SC2 model training and benchmarking. - Various strong baseline methods
sc2bench offers 7 input compression and 3 supervised compression baseline methods. - Diverse model options
sc2bench is built on PyTorch, torchdistill, CompressAI, and PyTorch Image Model, offering a lot of (backbone) models for SC2. - More than 180 trained models available
sc2bench offers a lot of trained models that you can conduct experiments, skipping a model (re)training step - Easy to design new experiments
torchdistill also helps users design modular, configuration-driven experiments, taking care of reproducibility in the experimental results.
The GitHub repository also provides example scripts. To learn more about sc2bench, see the repository and documentation.
How to Join the PyTorch Ecosystem
If you’re developing a project that supports the PyTorch community, you’re welcome to apply for inclusion in the Ecosystem. Please review the PyTorch Ecosystem review process to ensure that you meet the minimum expectations before applying.
Cheers!
The PyTorch Ecosystem Working Group