Introduction
The PyTorch community is actively working to build a growing ecosystem of specialized accelerators by offering a standardized and adaptable way for developers to add custom hardware support. As its adoption increases, the community is focusing on its long-term stability, clear referencing, and thorough documentation to foster wider collaboration and accelerate innovation.
OpenReg aims to achieve these goals by leveraging PrivateUse1 DispatchKey, which has emerged as the community-standard approach for external hardware integration.
OpenReg offers the following functionality:
- Test Backend: To serve as an in-tree test backend for PrivateUse1, ensuring quality stability through CI/CD.
- Integration Reference: To serve as a reference example for new backend integration.
- Integration Documentation: To provide module-level integration documentation that corresponds with the code.
Note:
The goal of OpenReg is not to implement a fully functional, high-performance PyTorch backend, but to serve as a minimalist reference implementation for mechanism verification.
Architecture
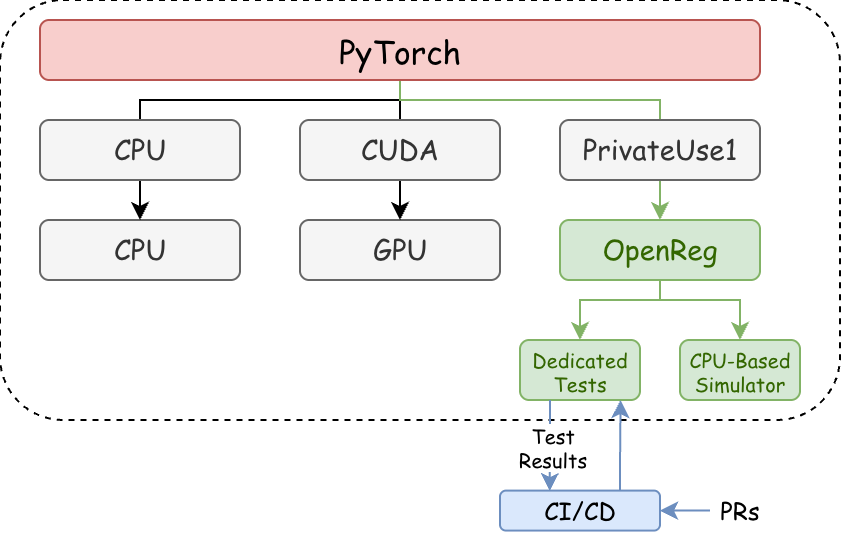
Architecture of OpenReg
The overall architecture of OpenReg can be separated into 3 aspects: a CPU-based simulator, CI/CD integration, and matching documents.
Simulator
OpenReg is designed as a standalone, self-contained PyTorch simulation backend. Its core purpose is to facilitate the integration of an accelerator with PyTorch’s computational graph and execution environment via PrivateUse1 DispatchKey, leveraging the PrivateUse1 device type for custom operations and device management. Key Components and Features:
- CPU-based Accelerator Simulator: OpenReg’s robust CPU-based accelerator simulator is essential for developing, testing, and debugging custom PyTorch operations and backend logic without immediate hardware access. It ensures functional correctness, enables early-stage development, and provides accurate performance predictions and resource utilization analysis before deployment.
- PyTorch Accelerator Integration Mechanism: OpenReg is a reference to integrate third-party hardware and software into PyTorch. It uses the PrivateUse1 device type for custom operators, kernels, and memory management, preventing conflicts and simplifying development for external vendors, thus expanding the PyTorch ecosystem.
CI/CD Integration
To ensure the stability, reliability, and consistent quality of accelerators, a comprehensive CI/CD strategy is being implemented.
- Migrate All Tests of Accelerator Integration Mechanism into OpenReg: All PrivateUse1-based accelerator integration tests will be moved into the OpenReg module, ensuring consistency, maintainability, and a single source of truth for all new integrations.
- Add OpenReg into CI/CD workflow: OpenReg has been fully integrated into existing CI/CD pipelines, automating tests, builds, and deployments with every code commit. This ensures code quality, identifies regressions, and maintains stability and functionality through unit, integration, and system-level tests.
Documentation
Comprehensive and accessible documentation is essential for the adoption and usability of OpenReg.
- Accelerator Integration Guide: Providing detailed guidance for developers to integrate their own accelerator into PyTorch, which contains Runtime, Operation Registration, and other high-level features.
Implementation
The implementation of OpenReg is located at pytorch/test/cpp_extensions/open_registration_extension/torch_openreg, and its file structure is as follows:
torch_openreg/ ├── csrc // Core device implementation │ ├── amp │ ├── aten // Operator registration │ │ ├── native │ └── runtime // Implementations for Host memory, device memory, Guard, etc │ └── ... ├── third_party // A C++ library that simulates a CUDA-like device using the CPU │ └── openreg └── torch_openreg // Python interface implementation ├── csrc // Python C++ binding code └── openreg // Python API └── ... |
Features
OpenReg is a reference implementation designed to integrate accelerators with PyTorch via PrivateUse1 seamlessly. It offers a comprehensive set of features, including:
- Operators Registration: OpenReg provides robust mechanisms for registering various types of operators:
- Built-in PyTorch Operators: Enables the registration of existing PyTorch operators, ensuring compatibility and leveraging the extensive PyTorch ecosystem.
- Custom Operators: Facilitates the integration of bespoke operators, allowing developers to extend PyTorch’s functionality with specialized computations.
- Fallback Mechanism: Implements a fallback system to gracefully handle cases where a registered operator is unavailable or unsuitable, ensuring continuous operation.
- Runtime Support: OpenReg provides comprehensive runtime support, encompassing essential features such as event management, stream handling, device management, execution guards, and Random Number Generation (RNG). This ensures fine-grained control and optimization over the execution environment.
- Cross-Platform Support: OpenReg supports Linux, macOS (OSX), and Windows operating systems.
- High-level Features:
- Auto Mixed Precision: Provides convenience methods for mixed precision, where some operations use torch.float32 datatype and other operations use lower precision floating point datatype: torch.float16 or torch.bfloat16.
- Autoload: When import torch, installed accelerators (such as torch_openreg) will be automatically loaded, achieving the same experience as the built-in backends.
Installation & Usages
OpenReg requires building from source, but this can be simply accomplished by running the following command:
cd test/cpp_extensions/open_registration_extension/torch_openreg python -m pip install --no-build-isolation -e . # for develop python -m pip install --no-build-isolation . # for install |
Using OpenReg is just as straightforward as using a CUDA device—all you need to do is declare your device with torch.device("openreg"), as shown in the code below:
import torch if not torch.openreg.is_available(): print("OpenReg backend is not available in this build.") exit() print("OpenReg backend is available!") device = torch.device("openreg") x = torch.tensor([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]], device=device) y = x + 2 print("Result y:\n", y) print(f"Device of y: {y.device}") z = y.cpu() print("Result z:\n", z) print(f"Device of z: {z.device}") |
Next Steps
OpenReg has a clear roadmap to enhance its capabilities within the PyTorch ecosystem. Future enhancements include distributed computing integration for large-scale models, ONNX support for interoperability, advanced compiler features for optimized performance, and comprehensive documentation for ease of adoption.
OpenReg is also being considered for inclusion in continuous integration (CI) pipelines as a critical testing backend. This would enable developers to verify hardware capabilities, ensure PyTorch’s stability and reliability (especially for out-of-tree backends), and accelerate development cycles by providing immediate feedback on changes.
Conclusion
By leveraging the CPU as a stand-in accelerator, OpenReg ensures PyTorch’s PrivateUse1 mechanism stays stable and reliable. It is both a safety net for the ecosystem and a reference guide for new hardware integrations. In essence, OpenReg is a forward-thinking project offering both enhanced functionalities and a robust testing mechanism for the evolving AI landscape and PyTorch ecosystem.
If you’re considering adding a new device backend to PyTorch, OpenReg is the place to start. It won’t replace the detailed work required for performance or scalability, but it provides a clear roadmap for setting up your device correctly.
If you’re interested in connecting with us and helping foster a more thriving PyTorch accelerator ecosystem, consider joining the Accelerator Integration Working Group, which is under the PyTorch Technical Advisory Council (TAC). This is the primary community forum for discussing and shaping the future of accelerator integration in PyTorch.