In this blog, we will briefly introduce torchtune, the Ascend backend, and demonstrate how torchtune can be used to fine-tune models with Ascend.
Introduction to Torchtune
Torchtune is a PyTorch-native library designed to simplify the fine-tuning of Large Language Models (LLMs). Staying true to PyTorch’s design principles, it provides composable and modular building blocks, as well as easily extensible training recipes. torchtune allows developers to fine-tune popular LLMs with different training methods and model architectures while supporting training on a variety of consumer-grade and professional GPUs.
You can explore more about torchtune’s code and tutorials here:
- GitHub Repository: The source code for torchtune is hosted on GitHub, where you can find the full implementation, commit history, and development documentation. Access the code repository here: Torchtune GitHub Repository
- Tutorials and Documentation: Torchtune provides detailed tutorials to help users quickly get started with the fine-tuning process and demonstrate how to use torchtune for various tasks like training and evaluation. You can access the official tutorials here: Torchtune Tutorials
In these resources, you’ll find not only how to fine-tune large language models using torchtune but also how to integrate with tools like PyTorch, Hugging Face, etc. They offer comprehensive documentation and examples for both beginners and advanced users, helping everyone customize and optimize their model training pipelines.
Introduction to Ascend Backend
Ascend is a series of AI computing products launched by Huawei, offering a full-stack AI computing infrastructure that includes processors, hardware, foundational software, AI computing frameworks, development toolchains, management and operation tools, as well as industry-specific applications and services. These products together create a powerful and efficient AI computing platform that caters to various AI workloads.
You can explore more about Ascend here: Ascend Community
How Torchtune Integrates with Ascend
Initially, devices were primarily matched using device strings. However, torchtune later introduced an abstraction layer for devices, leveraging the get_device_support() method to dynamically retrieve relevant devices based on the current environment.
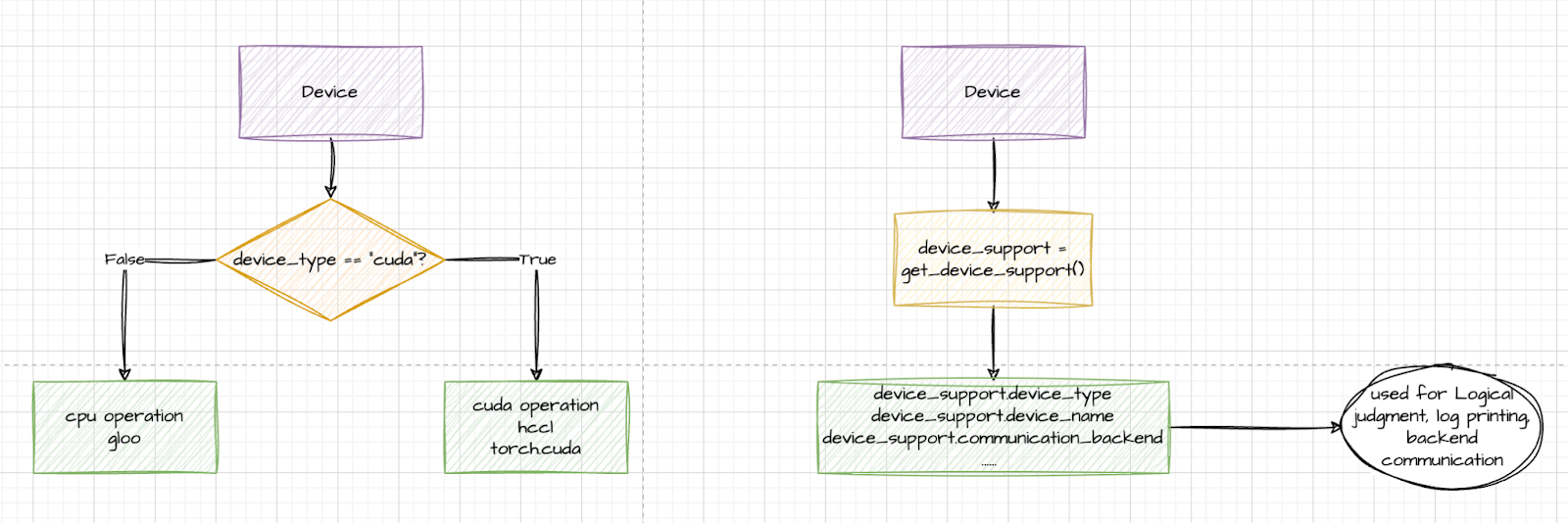
Ascend is seamlessly integrated into torchtune via the PrivateUse1 feature provided by PyTorch. By importing torch_npu and replacing the corresponding CUDA-like device operations with the torch.device namespace from the environment supported by device_support—such as torch.npu and torch.cuda—Ascend is effectively incorporated into torchtune. The PR is here.
torch_npu is a plugin developed for PyTorch, designed to seamlessly integrate Ascend NPU with the PyTorch framework, enabling developers to leverage the powerful computational capabilities of Ascend AI processors for deep learning training and inference. This plugin allows users to directly utilize Ascend’s computational resources within PyTorch without the need for complex migration or code changes.
Torchtune Quick Start with Ascend
In torchtune, there are two key concepts that are essential for customizing and optimizing the fine-tuning process: Config and Recipe. These concepts allow users to easily customize and optimize the fine-tuning process to suit different needs and hardware environments.
- Config is a file used by torchtune to configure the training process. It contains settings for the model, data, training parameters, and more. By modifying the Config file, users can easily adjust various aspects of the training process, such as data loading, optimizer settings, and learning rate adjustments. Config files are typically written in YAML format, making them clear and easy to modify.
- A Recipe in torchtune is a simple, transparent single-file training script in pure PyTorch. Recipes provide the full end-to-end training workflow but are designed to be hackable and easy to extend. Users can choose an existing Recipe or create a custom one to meet their fine-tuning needs.
When fine-tuning a model using the Ascend backend, torchtune simplifies the process by allowing you to specify the device type directly in the configuration file. Once you specify npu as the device type, torchtune automatically detects and utilizes the Ascend NPU for training and inference. This design allows users to focus on model fine-tuning without needing to worry about hardware details.
Specifically, you just need to set the relevant parameters in the Config file, indicating the device type as npu, such as:
# Environment
device: npu
dtype: bf16
# Dataset
dataset:
_component_: torchtune.datasets.instruct_dataset
source: json
data_files: ascend_dataset.json
train_on_input: False
packed: False
split: train
# Other Configs …
Once you’ve specified the npu device type in your configuration file, you can easily begin the model fine-tuning process. Simply run the following command, and torchtune will automatically start the fine-tuning process on the Ascend backend:
tune run <recipe_name> --config <your_config_file>.yaml
For example, if you’re using a full fine-tuning recipe (full_finetune_single_device) and your configuration file is located at ascend_config.yaml, you can start the fine-tuning process with this command:
tune run full_finetune_single_device --config ascend_config.yaml
This command will trigger the fine-tuning process, where torchtune will automatically handle data loading, model fine-tuning, evaluation, and other steps, leveraging Ascend NPU’s computational power to accelerate the training process.
When you see the following log, it means that the model has been fine-tuned successfully on the Ascend NPU.
……
dataset:
_component_: torchtune.datasets.instruct_dataset
data_files: ascend_dataset.json
packed: false
source: json
split: train
train_on_input: false
device: npu
dtype: bf16
enable_activation_checkpointing: true
epochs: 10
……
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Model is initialized with precision torch.bfloat16.
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Memory stats after model init:
NPU peak memory allocation: 1.55 GiB
NPU peak memory reserved: 1.61 GiB
NPU peak memory active: 1.55 GiB
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Tokenizer is initialized from file.
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Optimizer is initialized.
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Loss is initialized.
……
NFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Model checkpoint of size 4.98 GB saved to /home/lcg/tmp/torchtune/ascend_llama/hf_model_0001_9.pt
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Model checkpoint of size 5.00 GB saved to /home/lcg/tmp/torchtune/ascend_llama/hf_model_0002_9.pt
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Model checkpoint of size 4.92 GB saved to /home/lcg/tmp/torchtune/ascend_llama/hf_model_0003_9.pt
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Model checkpoint of size 1.17 GB saved to /home/lcg/tmp/torchtune/ascend_llama/hf_model_0004_9.pt
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Saving final epoch checkpoint.
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:The full model checkpoint, including all weights and configurations, has been saved successfully.You can now use this checkpoint for further training or inference.
10|20|Loss: 0.2997712790966034: 100%|██████████████████████████████| 2/2 [01:00<00:00, 30.03s/it]
Generating with Fine-Tuned Models
In the previous section, we used a fine-tuning dataset similar to identity.json, which is identity-related and made some adjustments to it.
In this section, we will use our model to perform some generation tasks. For this, we’ll use the generate recipe and the associated config.
Let’s first copy over the config to our local working directory so we can make changes.
tune cp generation ./ascend_generation_config.yaml
Let’s modify ascend_generation_config.yaml to include the following changes. Again, you only need to replace two fields: output_dir and checkpoint_files.
# Tokenizer
tokenizer:
_component_: torchtune.models.llama3.llama3_tokenizer
path: ${output_dir}/original/tokenizer.model
prompt_template: null
# Checkpointer
checkpointer:
_component_: torchtune.training.FullModelHFCheckpointer
checkpoint_dir: ${output_dir}
checkpoint_files: [
Hf_model_0001_0.pt,
……
hf_model_0004_9.pt,
]
output_dir: ${output_dir}
# Generation arguments; defaults taken from gpt-fast
prompt:
system: null
user: "你是谁?"
# Environment
device: npu
# Other Configs …
Next, we will run our generate recipe.
tune run generate --config ascend_generation_config.yaml
The results of the execution are as follows, and we can see that our assistant has learned to identify itself as the Torchtune Helper!
……
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:你是谁?您好,我是 Torchtune Helper,由 PyTorch 开发,旨在为用户提供智能化的回答和帮助。
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Time for inference: 4.75 sec total, 5.47 tokens/sec
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Bandwidth achieved: 89.18 GB/s
INFO:torchtune.utils._logging:Memory used: 0.00 GB