Scaling reinforcement learning (RL) for post-training large language models (LLMs) is notoriously difficult. While running RL on a single GPU or node is relatively simple, the complexity grows rapidly as you scale to hundreds of GPUs. Infrastructure challenges—distributed coordination, stability, reproducibility, and verification—often become the bottleneck, slowing down research and limiting how fast teams can iterate.
To solve this, the PyTorch team at Meta recently open-sourced torchforge, a PyTorch-native RL library built to make large-scale post-training dramatically easier. In collaboration with Stanford and CoreWeave, we put forchforge through its paces on a 512-GPU cluster, running GRPO at a scale and speed that would have been nearly impossible with existing tooling (jump to the code)—the outcome: streamlined setup, steady training, and an unambiguous route from idea to experiment.
In this blog, we’ll break down how torchforge simplifies RL infrastructure, how the partnership with Stanford and CoreWeave enabled experiments at scale, and what we learned from running RL with Weaver (A weak verifier system developed to address the gap between generation and verification in large language models.) as the verifier across hundreds of GPUs. We’ll also share results, practical insights, and recommendations for researchers aiming to scale their own RL post-training workflows.
tl;dr
We evaluated RL post-training across two model sizes—Qwen3-8B-Base and Qwen3-32B-Base—comparing three reward approaches:
- Single reward model (RM) (no annotations): Training with one reward model
- Weaver (no annotations): Training with Weaver’s aggregated verifier ensemble
- Annotated training samples: Oracle upper bound using ground-truth labels
Key findings on Math, GPQA, and MMLU Pro:
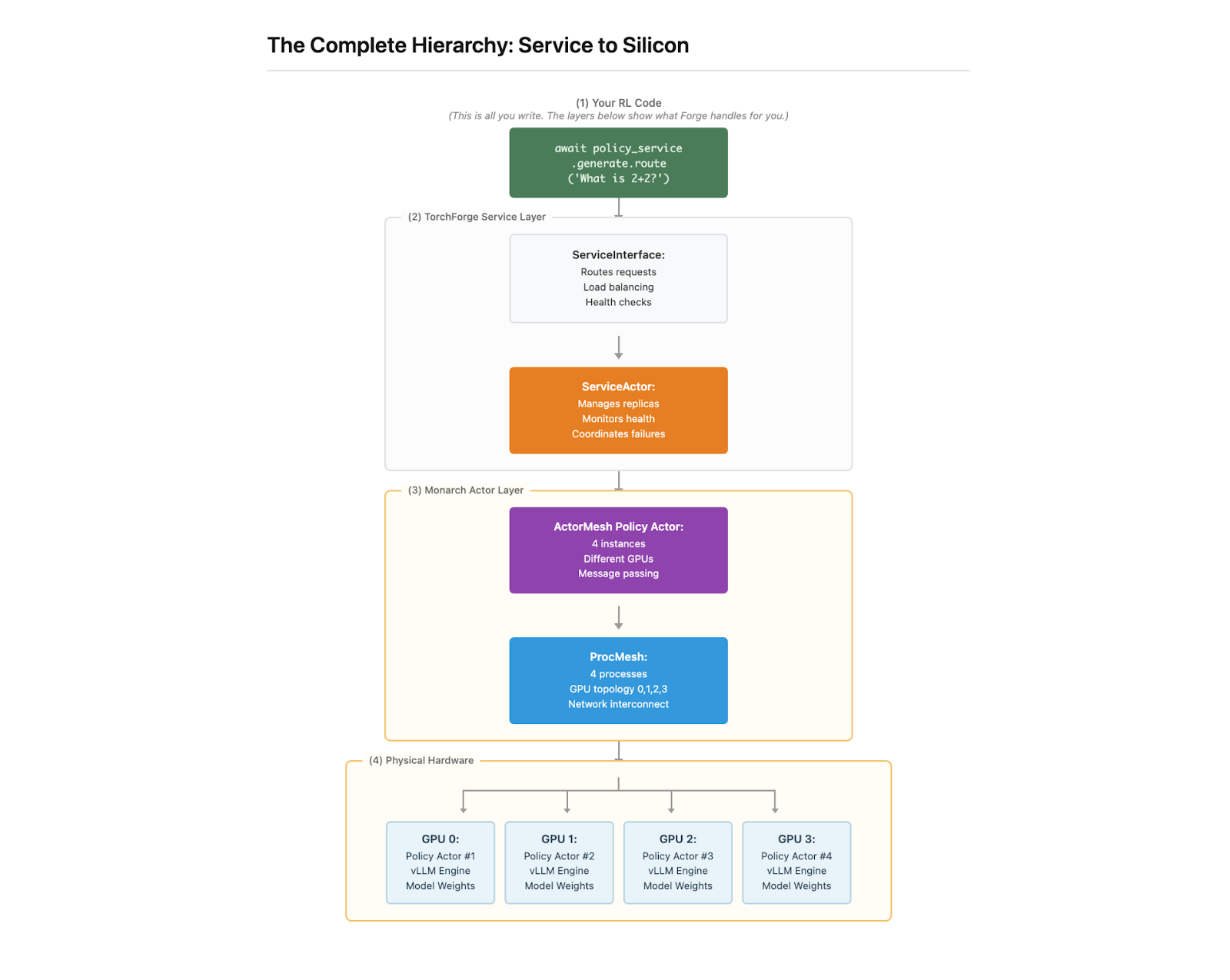
The combination of Forge + Weaver creates a complete RL infrastructure that was previously unavailable to the research community, lets understand these:
- Forge: provides PyTorch-native RL primitives that scale from single-node to a multi-node cluster without infrastructure complexity
- Weaver: delivers production-grade reward signals without human annotations or expensive API calls
- Monarch: orchestrates distributed coordination with automatic fault tolerance.
Together, this stack makes it practical to run RLVR (Reinforcement Learning with Verifier Rewards) at the scale needed for meaningful improvements on challenging reasoning benchmarks. Researchers can now iterate on reward design, policy updates, and verification strategies without rebuilding distributed systems from scratch.
torchforge: The Scalable RL Platform for LLMs
torchforge (“Forge”) is a PyTorch‑native library for scalable RL post‑training and agentic development that lets researchers focus on RL algorithms—not infrastructure. It expresses RL as clean, pseudocode‑like primitives while seamlessly scaling across GPU clusters and supporting any degree of asynchrony, from fully synchronous PPO to fully async off‑policy training. Built on proven distributed foundations, Forge separates infrastructure from algorithms so teams can iterate quickly on reward design, policy updates, and agent tooling without resharding logic, weight sync headaches, or control‑plane orchestration in their training code.
Under the hood, torchforge composes an ecosystem of production‑grade components—Monarch for distributed coordination and fault tolerance, TorchStore for fast in‑memory weight and tensor synchronization, vLLM for high‑throughput inference, and TorchTitan for scalable training—into a cohesive RL stack with clean service abstractions.
Key Features
- PyTorch‑native, pseudocode‑style RL APIs → write algorithms the way you’d sketch them on a whiteboard while Forge handles resource allocation, synchronization, and failure recovery—so you focus on research, not plumbing.
- Flexible synchronicity (sync PPO ↔ fully async off‑policy) → switch coordination patterns without touching rollout logic; reuse the same RL code across training paradigms.
- Monarch service abstractions with simple resource specs and adverbs like route() and fanout() → scale cleanly, load‑balance requests, broadcast when needed, and keep state via sticky sessions—all with automatic fault tolerance and zero retry boilerplate in your RL code.
- Decoupled control and data planes (Monarch + TorchStore) → services orchestrate routing/lifecycle while TorchStore performs RDMA‑accelerated, DTensor‑native tensor movement; GPUs keep generating while weights synchronize, eliminating lockstep and boosting throughput.
- TorchStore in‑memory, topology‑aware weight sync → fast, efficient resharding and tensor IO; decouple training from generation for truly asynchronous pipelines across nodes and clusters.
- Proven components end‑to‑end → vLLM for high‑throughput inference (PagedAttention, continuous batching) and TorchTitan for scalable training (FSDP, pipeline/tensor parallelism), yielding higher efficiency without bespoke integration work.
- Heterogeneous, ephemeral scaling → independently scale policy inference, reward models, and CPU‑only tools; bring environments up with the job and tear them down on completion—no separate Kubernetes deployments required.
- Simple integration of custom rewards and verifiers (e.g., Weaver) → adopt RLVR‑style patterns and new objective signals quickly, without standing up one‑off infrastructure per verifier.
- Robust, reproducible pipelines by design → clean separation of algorithm logic from infra, consistent coordination patterns (sync or async), and automatic fault handling reduce flakiness and speed iteration.
- Agentic extensibility via first‑class environments and tools → start with sandboxed code execution and expand to richer “Open Environments” integrations for complex agent workflows and simulations.
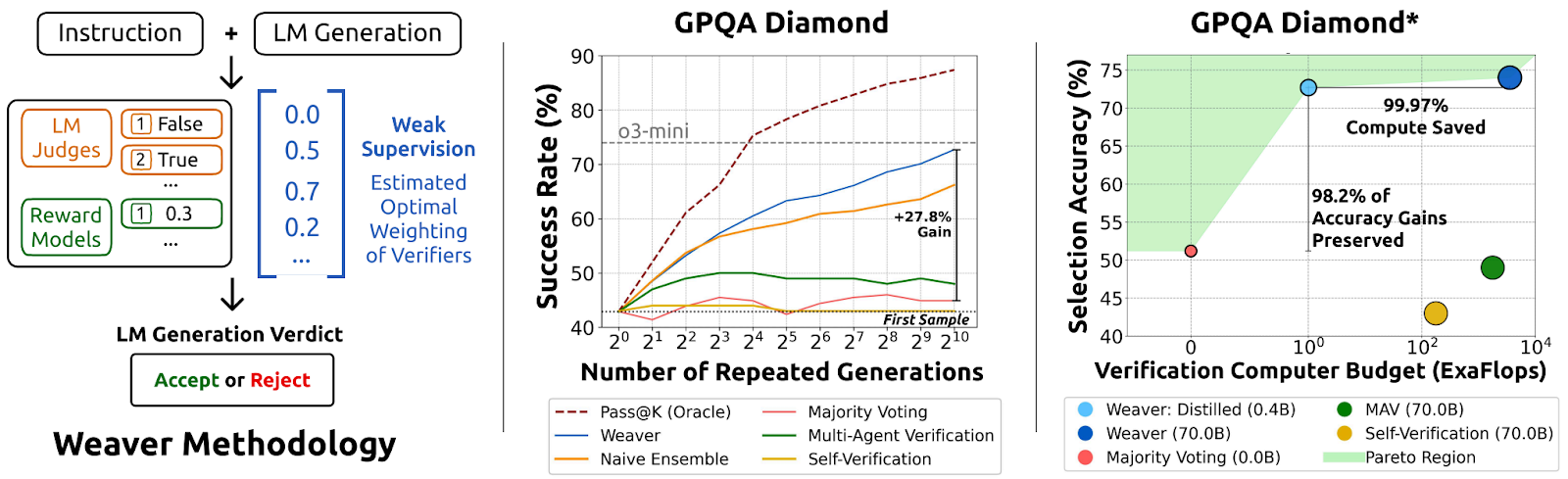
Weaver To Forge : A Verifier for Reasoning Experimentation
In reinforcement learning for LLMs, verifiers serve as the reward function—the critical signal that tells the model which generations are good and which need improvement. Weaver’s role in RL pipelines:
- Reward Signal Provider: Evaluates candidate model outputs and provides scalar rewards based on correctness probability
- Enables RLVR (Reinforcement Learning with Verifier Rewards): Allows RL training without expensive human preference data
- Scales to Complex Reasoning: Provides reliable signals on difficult tasks like mathematical proofs and scientific reasoning where simple string-matching fails
- Process-Level Feedback: Can evaluate intermediate reasoning steps, not just final answers
A core part of RL loops is verifiers, there are many manual, heuristic and algorithmic approaches which we can use part of the loop. For the large scale experiments on CoreWeave, we chose to use Weaver as our framework of choice.
What is Weaver?
Weaver is a weak verifier system designed to close the generation-verification gap in large language models. The core problem it addresses is that LLMs often generate correct answers but struggle to reliably identify which of their responses are actually correct. It is built on the principle that diverse verifiers offer complementary signals for correctness. The project demonstrates that you don’t need perfect verifiers—you need a smart way to combine imperfect ones.
Rather than relying on expensive frontier models or extensive human labeling, Weaver takes a fundamentally different approach: it aggregates multiple smaller, weak verifiers (such as reward models and LM judges) to create a powerful verification engine. Think of it like a jury system—individual verifiers may be noisy or biased, but their collective agreement patterns reveal which answers are truly correct.
- Automated: Eliminates continuous human annotation and reduces dependence on expensive frontier model APIs (like GPT-4 as a judge)
- Scalable: The distilled 400M Weaver model verifies thousands of generations per second, supporting high-throughput RL where you generate 100+ candidates per query while integrating seamlessly with distributed infrastructure like Forge
- Reliable: Statistical aggregation reduces single-verifier bias, provides calibrated confidence scores (not just binary accept/reject), and generalizes across reasoning domains—preventing reward hacking, quality misjudgments, and the need for massive human feedback datasets
To validate the full pipeline at scale, we evaluate on MATH500, GPQA Diamond, and MMLU Pro—matching frontier model performance (o3‑mini). The system trains without labeled data, learning from weak supervision via verifier‑agreement signals. For deployment, we distill the ensemble into a compact 400M‑parameter model that preserves 98.7% of ensemble accuracy while cutting inference compute by 99.97%. For more information on the Weaver methodology, please check out the blog post and NeurIPS 2025 paper.
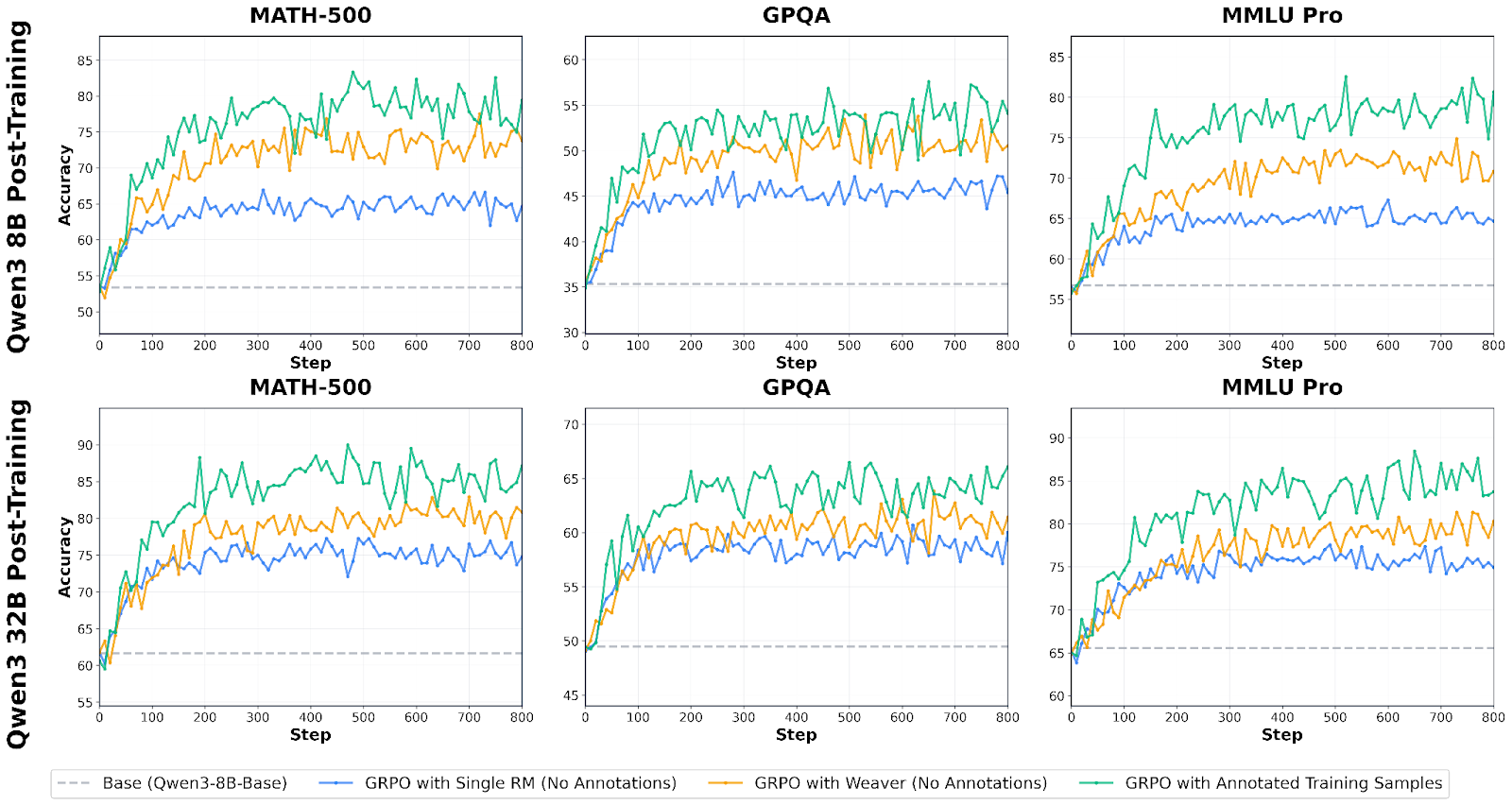
Benchmarks with Weaver Scoring:
Training with Weaver-based rewards shows substantial improvements across math, science, and reasoning tasks. We evaluated scaling behavior across two model sizes—Qwen3-8B-Base and Qwen3-32B-Base—comparing three reward approaches:
- Single RM (No Annotations): Training with one reward model
- Weaver (No Annotations): Training with Weaver’s aggregated verifier ensemble
- Annotated Training Samples: Oracle upper bound using ground-truth labels
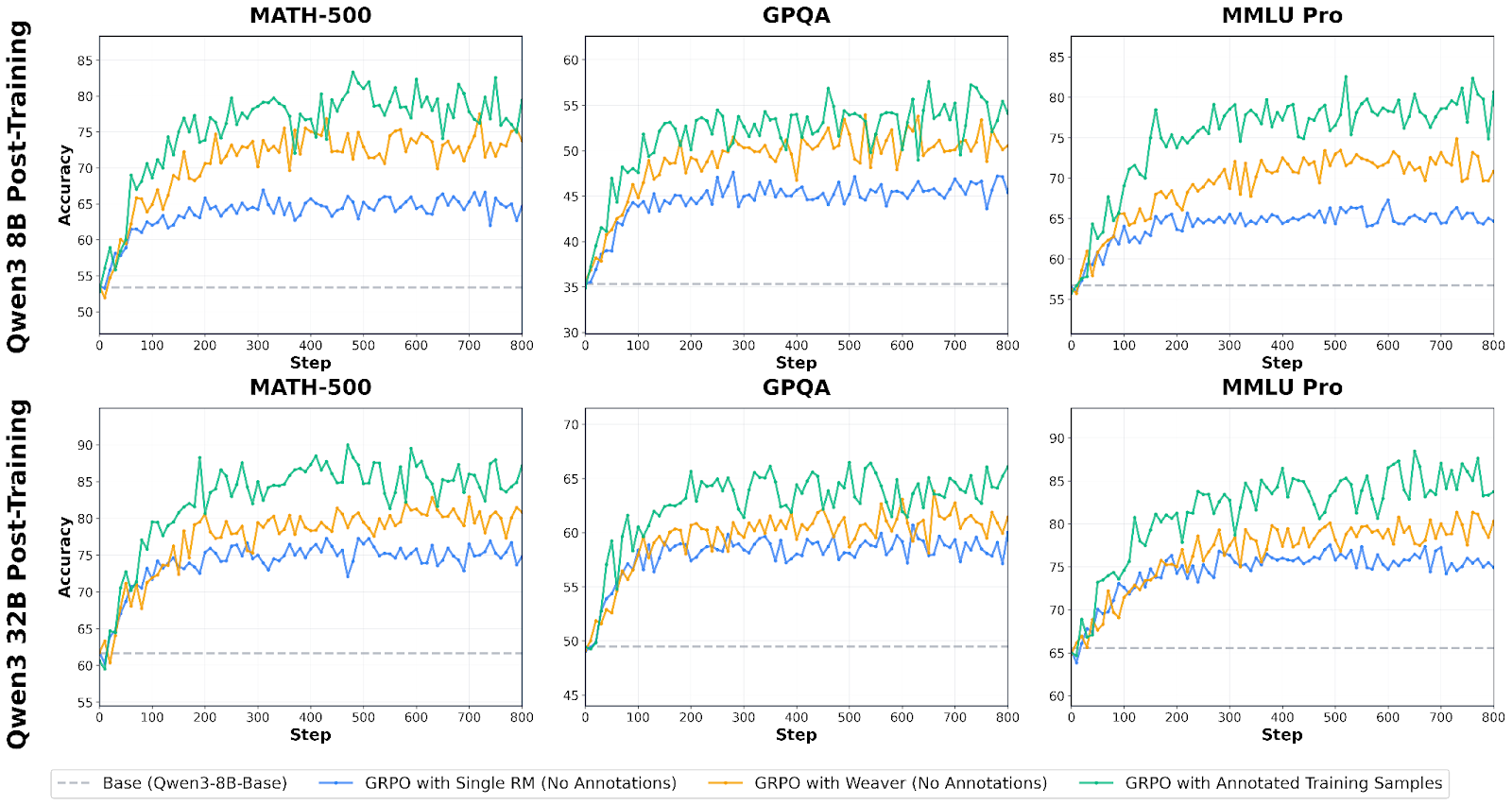
Key Findings on Math, GPQA, and MMLU Pro:
Our Pipeline significantly outperforms single reward models across all benchmarks and both model scales:
-
- On Qwen3-8B: Our pipeline using Weaver achieves 63% of the gap from single RM to annotated training on GPQA, 65% on MATH-500, and 50% on MMLU Pro
- On Qwen3-32B: Weaver captures 54% of the gap on GPQA, 44% on MATH-500, and 35% on MMLU Pro
- No human annotations required: Weaver achieves these gains using only unlabeled verifier agreement patterns
- Consistent scaling behavior: The advantage of Weaver over single RM holds across both 8B and 32B models, demonstrating that weak verifier aggregation provides value regardless of base model capability
- Shrinks the verification gap: On MATH-500, Weaver reaches 77.5% accuracy on 8B (within 5.8 points of annotated) and 82.9% on 32B (within 7.1 points of annotated)—substantially narrowing the gap to fully supervised training
- Production-Scale Infrastructure Results
- The Meta/Stanford collaboration on Forge pushed this stack to its limits on CoreWeave’s 512 GPU cluster, achieving reliability and performance metrics that bridge the gap between academic research and production AI systems.
- Reliability at Scale
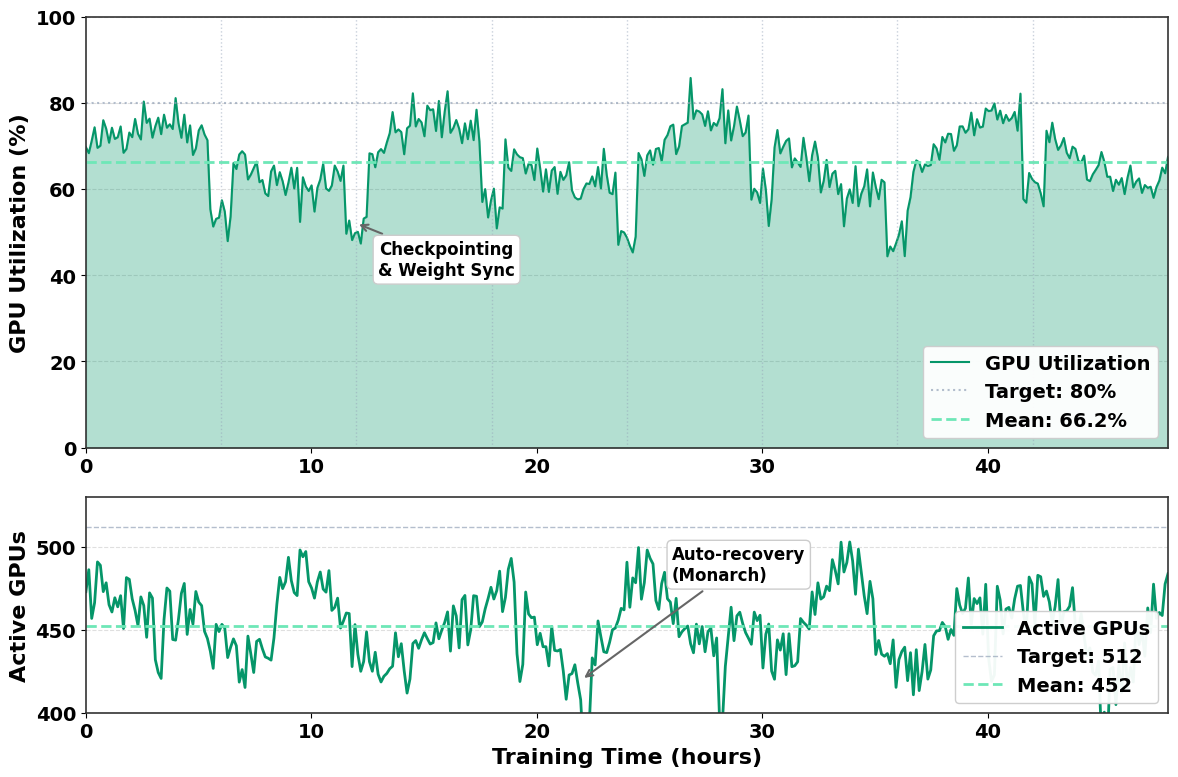
- Zero hardware failures across hundreds of hours of continuous training
- >90% job completion rate without manual intervention—Monarch’s automatic fault recovery handled transient failures transparently
- Efficiency Gains
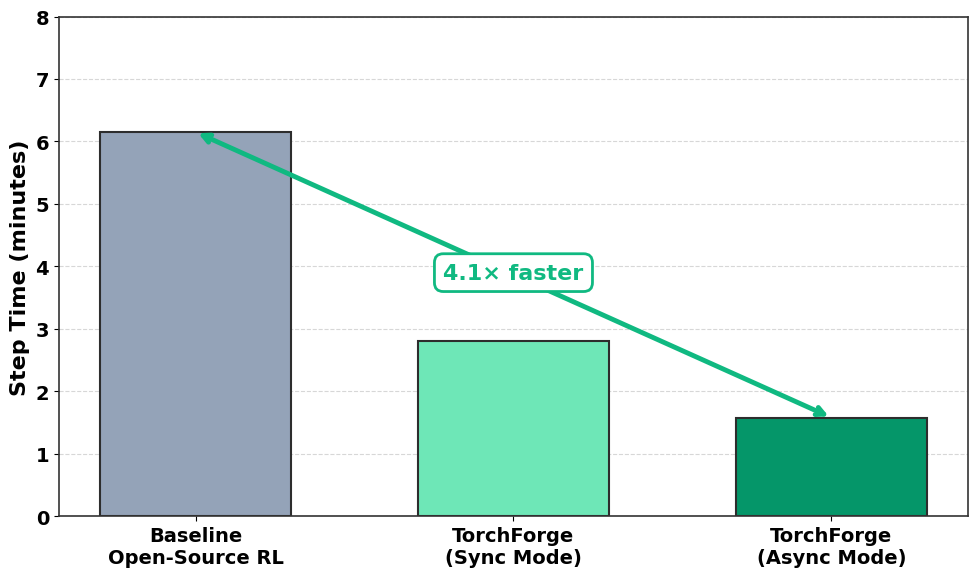
- 4x faster iteration: Compared to alternative open-source RL frameworks, step times improved from 6 minutes → 1.5 minutes by decoupling generation, verification, and training
- >65% GPU utilization: Efficient scheduling minimized idle time despite complex multi-phase RL workloads
- High-throughput verification: Weaver’s distilled model enabled evaluation of 100 generations per query without becoming the bottleneck
Scaling RL on CoreWeave
We validated Forge and Weaver end to end on a CoreWeave Kubernetes Service (CKS) cluster with NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand. RL at scale requires orchestrating separate stacks, managing sharding, and efficiently transferring weights. CoreWeave provided the ideal environment for Forge and Weaver with its Slurm-on-Kubernetes (SUNK) offering.
Through the torchx SLURM scheduler, Forge is able to schedule all of the required workloads and services that are used in the RL training loop while leveraging the CoreWeave node health monitoring and automation. SUNK transparently manages all of the network topology metadata needed to guarantee the most optimal placement of the workloads themselves. This engineering integration ensures the infrastructure remains seamless, allowing researchers to concentrate entirely on the RL algorithm, reward design, and the environment.
By minimizing infrastructure concerns and providing a reliable scheduler:
- Forge and SUNK manage scaling, routing, load balancing, and fault tolerance behind the scenes.
- This translates directly into faster job startup and higher end-to-end throughput for the large asynchronous rollouts and training loops required for RLVR (Reinforcement Learning with Verifier Rewards).
Getting Started
- Where to find Forge (GitHub repo, documentation, discord).
- How to use Weaver as a verifier in your own RL experiments.
- Resources for deploying Monarch for distributed training.
- Guidance for running Forge at scale, including on cloud clusters like CoreWeave.
Call to Action: Build With Us
- The future of LLM reasoning lies in scalable verification, not just bigger models. We’re excited to see what the community builds with these tools:
- Weaver: Integrate weak verifier aggregation into your RL experiments
- TorchForge: Start building scalable RL pipelines with clean, PyTorch-native APIs
- Monarch: Deploy distributed training with built-in fault tolerance
- 💻 GitHub
torchforge on SUNK: Get started with Forge on CoreWeave.
-
- We Want Your Contributions
- New verifiers: Share reward models, LM judges, or specialized critics for different domains on OpenEnv, which can be used for Weaver or other RLVR approaches!
- Novel RL algorithms: Implement your own policy update rules on top of Forge’s flexible primitives
- Scaling experiments: Run Weaver on new benchmarks and report what works (and what doesn’t!)
- Infrastructure improvements: Help optimize the data plane, improve fault tolerance, or add new service abstraction.
- Join the Conversation
- Open issues on GitHub with questions, bug reports, or feature requests
- Share your results—we’re building a community knowledge base of what verification strategies work best
- Collaborate with us on extending this stack to agentic workflows, code generation, and beyond
- Let’s keep shrinking generation-verification gap together!