PyTorch revolutionized how we build and serve AI models, but getting them to production remains challenging. Data inconsistencies between training and serving environments are one of the primary challenges AI models face in getting into production, what the AI industry has coined “training-serving skew.” Even the most impactful models fail when production data doesn’t match the data the model was trained on.
We’re thrilled to announce that Feast — an open-source feature store for production AI— has officially joined the PyTorch Ecosystem! By aligning Feast with the PyTorch community, we’re combining PyTorch’s modeling excellence with robust data infrastructure practices, enabling seamless transitions from model development to production deployment.
To view the PyTorch Ecosystem, see the PyTorch Landscape and learn more about how projects can join the PyTorch Ecosystem.
About Feast
Feast (short for Feature Store) is designed to manage data for production-scale AI. It offers a unified API for defining, storing, and serving data (i.e., features), bridging offline (training) and online (serving).
What makes Feast particularly valuable for PyTorch workflows is its ability to eliminate training-serving skew—ensuring production models receive the exact same feature transformations used during training. At its core, Feast provides:
- Declarative feature definitions – Define features once, use them consistently across training and serving
- Point-in-time correctness – Prevents data leakage during training by managing historical feature states
- Pluggable architecture – Adapts to your existing data infrastructure without requiring major changes (integrations with Spark, Snowflake, BigQuery, Ray, Kubernetes and cloud-native storage/serving layers)
- Low-latency serving – Pre-computed features stored for sub-millisecond retrieval during inference
- Python-first APIs – Seamlessly integrates with PyTorch workflows and MLOps pipelines
Feast isn’t a modeling library — it provides the data foundation that ensures your models perform consistently from development to production. By joining the PyTorch Ecosystem, Feast reinforces its commitment to open, interoperable AI infrastructure that scales with the community’s needs.
By joining the PyTorch Ecosystem, Feast reinforces its commitment to open, interoperable AI infrastructure that scales with the community’s needs.
See It In Action: Sentiment Analysis with Feast + PyTorch
See how Feast works with PyTorch. Try our sentiment analysis demo that showcases real-time feature serving with zero setup.
What you’ll learn:
- How to define and serve features for PyTorch models
- Real-time feature retrieval for model inference
- Point-in-time correct feature engineering for training
This demo shows how to build a complete sentiment analysis pipeline using Hugging Face transformers, synthetic text data, and Feast’s feature store. You’ll see how Feast manages features consistently from training to real-time inference—all running locally with SQLite, no infrastructure required.
Step 1: Installation and Setup
First, we’ll install the Python package, jump-start the demo, and apply the metadata using the Feast CLI tool.
pip install feast[pytorch]>=0.58.0 feast init pytorch_demo -t pytorch_nlp
By running feast init, we initiate a template repository with a sentiment embedding transformer. The directory structure will look like this:
> tree . ├── __init__.py ├── feature_repo │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── data │ │ └── sentiment_data.parquet │ ├── example_repo.py │ ├── feature_store.yaml │ ├── static_artifacts.py │ └── test_workflow.py └── README.md
Here’s a brief summary of the purpose of each file:
-
README.md– provides a detailed summary of the demo project -
feature_repo/__init__.py– a file needed to recognize the python project -
feature_repo/data/sentiment_data.parquet– sample data for this demo -
feature_repo/example_repo.py– declarative code with all of our features, transformations, and other Feast objects -
feature_repo/static_artifacts.py– this is code used by Feast to load the small sentiment model at build time for better latency -
feature_repo/test_workflow.py– this is an end-to-end demo script that runs through the MLOps pipeline.
The sentiment_data.parquet file provides a set of sample data with labels and a sentiment score. A transposed subsample of the data looks like so:
| | 0 | 1 | |:---------------------|:---------------------|:---------------------| | text_id | text_0000 | text_0001 | | user_id | user_028 | user_059 | | text_content | Having an amazing... | Traffic is horrib... | | sentiment_label | positive | negative | | sentiment_score | 0.993 | 0.982 | | text_length | 48 | 59 | | word_count | 9 | 10 | | exclamation_count | 1 | 1 | | caps_ratio | 0.021 | 0.017 | | emoji_count | 0 | 0 | | event_timestamp | 2025-12-15 16:38:... | 2025-12-03 15:08:... | | created | 2025-12-23 14:40:... | 2025-12-23 14:40:... | | user_avg_sentiment | 0.927 | 0.902 | | user_text_count | 11 | 7 | | user_avg_text_length | 47.636 | 51.429 |
Next we will change directories into feature_repo where we can store all of our declarative feature code to serve our application. Then we will run feast apply, which will register the declarative code (Entities, Feature Views, and other Feast-specific objects) as metadata to the Feast feature registry, which is used for governance, lineage, and cataloging.
cd pytorch_demo/feature_repo feast apply
The output will look like the below:
Created entity text Created entity user Created feature view text_features Created feature view user_stats Created on demand feature view sentiment_prediction Created feature service sentiment_analysis_v1 Created feature service sentiment_analysis_v2
Now that we have registered our metadata, we can take our sample data and upload it to our “Online” database to serve for production use cases.
Step 2: Load data to the Online Database
We can upload our data to our online database by using the Feast CLI tool, which supports local file upload via the materialize-incremental command. For this demo, we use SQLite, but Feast supports a wide variety of production-grade enterprise databases.
feast materialize-incremental $(date -u +"%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")
Step 3: Start and test REST API
Using the Feast CLI tool again, we can spin up the feature server, which exposes REST API endpoints that allow other services to securely access the data we uploaded in our online database.
feast serve --host 0.0.0.0 --port 6566
We can make a curl request in a separate terminal session:
curl -X POST \ "http://localhost:6566/get-online-features" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "features": [ "sentiment_prediction:predicted_sentiment", "sentiment_prediction:sentiment_confidence", "sentiment_prediction:positive_prob" ], "entities": { "input_text": ["I love this amazing product!", "This service is terrible"], "model_name": ["cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest", "cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest"] } }' | jq
And you will see a nicely structured JSON with our feature data, including data that was transformed on the fly (i.e., “on demand”) with Feast! This data can be used for various applications, particularly those running inference for Recommendation Engines, Scorecard models, RAG applications, and other AI use cases.
Step 4: Render UI to see Data Lineage
Finally, we can spin up the UI locally to see the metadata from the registry rendered nicely. The Feast UI is a catalog meant to centralize features to enable cross-team collaboration and reduce feature re-implementation.
You can run the UI using the Feast CLI via and navigate to the lineage page to see the rich visualization.
feast ui
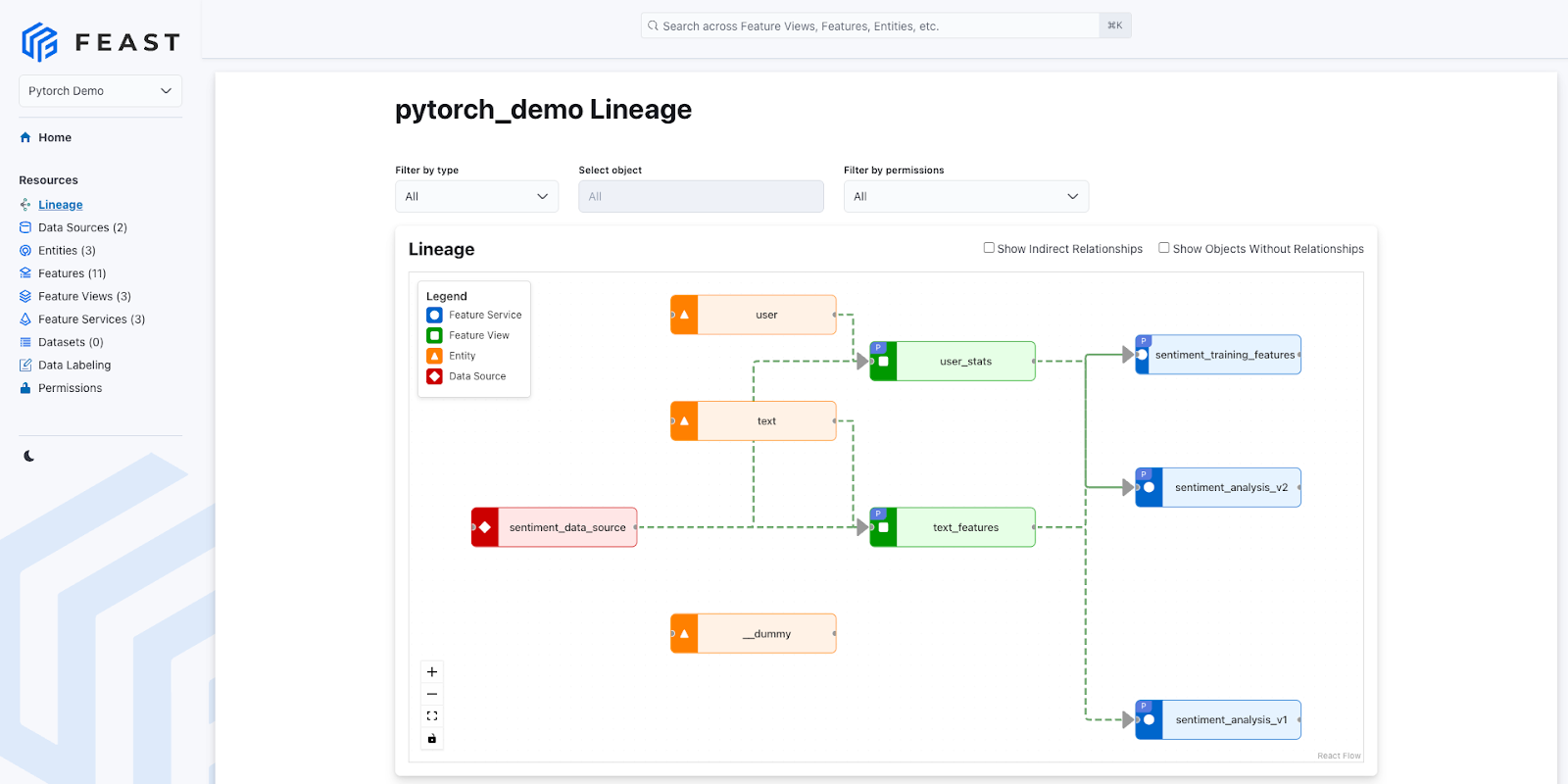
Example of Feast’s Lineage UI
Beyond the demo, Feast supports additional functionality to empower AI/ML teams to ship production grade AI applications.
Compute Engine and Training Dataset Preparation
During feature development and iteration (i.e., training dataset preparation), users typically have to run a batch process to backfill their historical data. Feast supports point-in-time joins to ensure Feature correctness and to avoid leaking future feature information into the training data. To do this, Feast uses a Compute Engine abstraction that supports multiple providers (local, Spark, Snowflake, Lambda, Flink, and Ray). This flexibility allows our end users to leverage the best of open source while providing a simple SDK that avoids frequently occurring challenges.
Open Telemetry for Observability
Feast supports OpenTelemetry and provides comprehensive monitoring and observability for your feature serving infrastructure.
Authorization/RBAC and Permissions for Governance
Feast supports both OIDC authentication and Kubernetes RBAC for robust Role Based Access Control. Additionally, Feast supports a Permission system to allow fine-grained permission policies for the online store, offline store, and registry.
How Feast Enhances the PyTorch Experience
Integrating Feast into the PyTorch ecosystem unlocks several critical benefits for practitioners building production AI systems:
- Eliminates Training-Serving Skew – The #1 cause of model performance degradation in production. Feast ensures your model receives identical feature transformations during training and inference, maintaining model accuracy at scale.
- Accelerates Model Deployment – Pre-computed features stored in optimized databases enable the real-time serving of data with sub-millisecond latency for real-time inference. No more waiting for feature computation during inference.
- Enables Feature Reuse Across Teams – Centralized feature definitions prevent redundant work. When one team creates user behavior features for a recommendation model, other teams can reuse them for fraud detection or personalization models.
- Powers Advanced AI Workflows – Feast’s vector store capabilities, combined with PyTorch, enable sophisticated retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines where document embeddings are retrieved and used to enhance large language model responses.
- Provides Production-Grade Governance – Built-in lineage tracking, access controls, and monitoring ensure your PyTorch models meet enterprise requirements for data governance and compliance.
Community-Proven at Scale
Trusted by organizations like NVIDIA, Shopify, and other companies building production PyTorch systems across industries from e-commerce to financial services.
Real-World Impact
Feast has gained traction across industries, powering AI applications at both startups and enterprises. Consider these use cases:
- Real-time Personalization: E-commerce platforms use Feast to serve up-to-date user behavior features to PyTorch recommendation models, enabling personalized product suggestions with millisecond response times.
- Financial AI: Credit underwriting systems leverage Feast’s point-in-time correctness to ensure PyTorch models for fraud detection aren’t trained with future information, maintaining model accuracy and regulatory compliance.
- RAG Applications: Organizations combine Feast with PyTorch-based language models to implement retrieval-augmented generation, where relevant documents are retrieved from vector stores and used to provide contextually-appropriate responses.
Call to Action
If you’re working with PyTorch (or exploring model deployment or RAG workflows), we invite you to start exploring Feast today:
- Visit the Feast website: https://feast.dev Feast
- Read the docs: https://docs.feast.dev docs.feast.dev
- Check out the GitHub repo: https://github.com/feast-dev/feast GitHub
- Join our community: whether you want to add a new connector, improve documentation, or integrate Feast into your PyTorch stack — contributions are welcome.
Ready to supercharge your PyTorch workflows with Feast? Install Feast with PyTorch support:
pip install feast[pytorch]>=0.58.0
Conclusion
The integration of Feast into the PyTorch Ecosystem represents a significant step forward in making production-ready AI more accessible. By combining PyTorch’s modeling capabilities with Feast’s robust data management, developers can now build end-to-end AI systems that scale from prototype to production with confidence.