Concepts
Engine
The essence of the framework is the class Engine, an abstraction that loops a given number of times over
provided data, executes a processing function and returns a result:
while epoch < max_epochs:
# run an epoch on data
data_iter = iter(data)
while True:
try:
batch = next(data_iter)
output = process_function(batch)
iter_counter += 1
except StopIteration:
data_iter = iter(data)
if iter_counter == epoch_length:
break
Thus, a model trainer is simply an engine that loops multiple times over the training dataset and updates model parameters. Similarly, model evaluation can be done with an engine that runs a single time over the validation dataset and computes metrics. For example, model trainer for a supervised task:
def update_model(trainer, batch):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
x, y = prepare_batch(batch)
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return loss.item()
trainer = Engine(update_model)
trainer.run(data, max_epochs=100)
Note
By default, epoch length is defined by len(data). However, user can also manually define the epoch length as a number of iterations to loop. In this way the input data can be an iterator.
trainer.run(data, max_epochs=100, epoch_length=200)
Events and Handlers
To improve the Engine’s flexibility, an event system is introduced that facilitates interaction on each step of
the run:
engine is started/completed
epoch is started/completed
batch iteration is started/completed
Complete list of events can be found at Events.
Thus, user can execute a custom code as an event handler. Let us consider in more detail what happens when
run() is called:
fire_event(Events.STARTED)
while epoch < max_epochs:
fire_event(Events.EPOCH_STARTED)
# run once on data
for batch in data:
fire_event(Events.ITERATION_STARTED)
output = process_function(batch)
fire_event(Events.ITERATION_COMPLETED)
fire_event(Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED)
fire_event(Events.COMPLETED)
At first engine is started event is fired and all this event handlers are executed (we will see in the next paragraph how to add event handlers). Next, while loop is started and epoch is started event occurs, etc. Every time an event is “fired”, attached handlers are executed.
Attaching an event handler is simple using method add_event_handler() or
on() decorator:
trainer = Engine(update_model)
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.STARTED, lambda engine: print("Start training"))
# or
@trainer.on(Events.STARTED)
def on_training_started(engine):
print("Another message of start training")
# attach handler with args, kwargs
mydata = [1, 2, 3, 4]
def on_training_ended(engine, data):
print("Training is ended. mydata={}".format(data))
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.COMPLETED, on_training_ended, mydata)
Event handlers can be detached via remove_event_handler() or via the RemovableEventHandler
reference returned by add_event_handler(). This can be used to reuse a configured engine for multiple loops:
model = ...
train_loader, validation_loader, test_loader = ...
trainer = create_supervised_trainer(model, optimizer, loss)
evaluator = create_supervised_evaluator(model, metrics={'acc': Accuracy()})
def log_metrics(engine, title):
print("Epoch: {} - {} accuracy: {:.2f}"
.format(trainer.state.epoch, title, engine.state.metrics['acc']))
@trainer.on(Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED)
def evaluate(trainer):
with evaluator.add_event_handler(Events.COMPLETED, log_metrics, "train"):
evaluator.run(train_loader)
with evaluator.add_event_handler(Events.COMPLETED, log_metrics, "validation"):
evaluator.run(validation_loader)
with evaluator.add_event_handler(Events.COMPLETED, log_metrics, "test"):
evaluator.run(test_loader)
trainer.run(train_loader, max_epochs=100)
Event handlers can be also configured to be called with a user pattern: every n-th events, once or using a custom event filtering function:
model = ...
train_loader, validation_loader, test_loader = ...
trainer = create_supervised_trainer(model, optimizer, loss)
@trainer.on(Events.ITERATION_COMPLETED(every=50))
def log_training_loss_every_50_iterations(engine):
print("{} / {} : {} - loss: {:.2f}"
.format(engine.state.epoch, engine.state.max_epochs, engine.state.iteration, engine.state.output))
@trainer.on(Events.EPOCH_STARTED(once=25))
def do_something_once_on_25_epoch(engine):
# do something
def custom_event_filter(engine, event):
if event in [1, 2, 5, 10, 50, 100]:
return True
return False
@engine.on(Events.ITERATION_STARTED(event_filter=custom_event_filter))
def call_on_special_event(engine):
# do something on 1, 2, 5, 10, 50, 100 iterations
trainer.run(train_loader, max_epochs=100)
Note
User can also register custom events with register_events(), attach handlers and fire custom events
calling fire_event() in any handler or process_function.
See the source code of create_supervised_tbptt_trainer for an example of usage of
custom events.
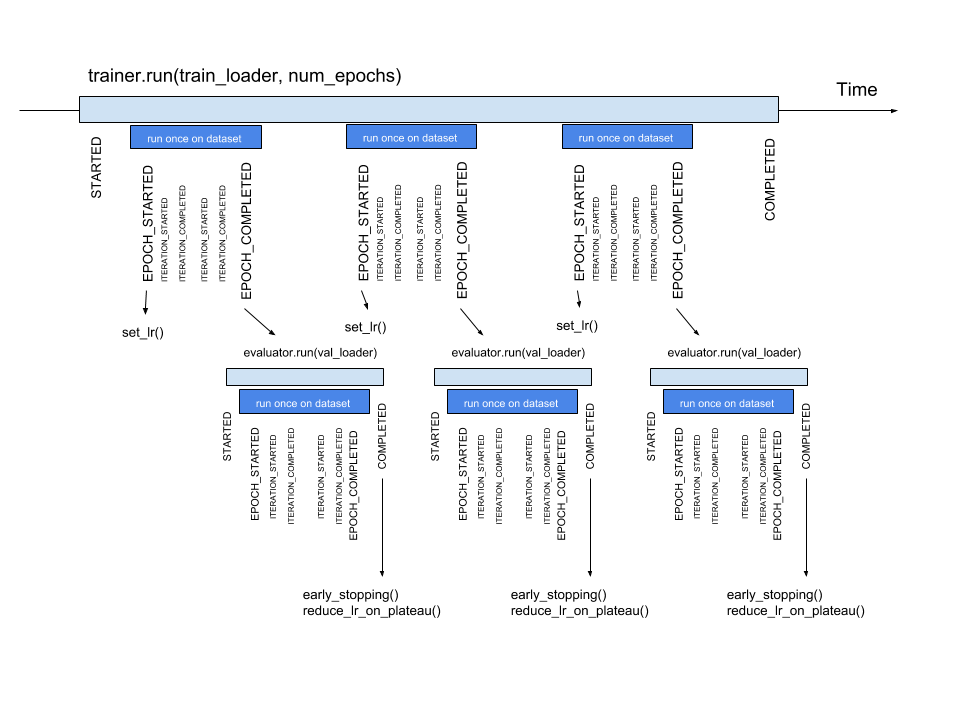
Timeline and events
Below the events and some typical handlers are displayed on a timeline for a training loop with evaluation after every epoch:
State
A state is introduced in Engine to store the output of the process_function, current epoch,
iteration and other helpful information. Each Engine contains a State,
which includes the following:
engine.state.seed: Seed to set at each data “epoch”.
engine.state.epoch: Number of epochs the engine has completed. Initializated as 0 and the first epoch is 1.
engine.state.iteration: Number of iterations the engine has completed. Initialized as 0 and the first iteration is 1.
engine.state.max_epochs: Number of epochs to run for. Initializated as 1.
engine.state.output: The output of the process_function defined for the
Engine. See below.etc
Other attributes can be found in the docs of State.
In the code below, engine.state.output will store the batch loss. This output is used to print the loss at every iteration.
def update(engine, batch):
x, y = batch
y_pred = model(inputs)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return loss.item()
def on_iteration_completed(engine):
iteration = engine.state.iteration
epoch = engine.state.epoch
loss = engine.state.output
print("Epoch: {}, Iteration: {}, Loss: {}".format(epoch, iteration, loss))
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.ITERATION_COMPLETED, on_iteration_completed)
Since there is no restrictions on the output of process_function, Ignite provides output_transform argument for its
metrics and handlers. Argument output_transform is a function used to transform engine.state.output for intended use. Below we’ll see different types of engine.state.output and how to transform them.
In the code below, engine.state.output will be a list of loss, y_pred, y for the processed batch. If we want to attach Accuracy to the engine, output_transform will be needed to get y_pred and y from
engine.state.output. Let’s see how that is done:
def update(engine, batch):
x, y = batch
y_pred = model(inputs)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return loss.item(), y_pred, y
trainer = Engine(update)
@trainer.on(Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED)
def print_loss(engine):
epoch = engine.state.epoch
loss = engine.state.output[0]
print ('Epoch {epoch}: train_loss = {loss}'.format(epoch=epoch, loss=loss))
accuracy = Accuracy(output_transform=lambda x: [x[1], x[2]])
accuracy.attach(trainer, 'acc')
trainer.run(data, max_epochs=10)
Similar to above, but this time the output of the process_function is a dictionary of loss, y_pred, y for the processed batch, this is how the user can use output_transform to get y_pred and y from engine.state.output. See below:
def update(engine, batch):
x, y = batch
y_pred = model(inputs)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return {'loss': loss.item(),
'y_pred': y_pred,
'y': y}
trainer = Engine(update)
@trainer.on(Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED)
def print_loss(engine):
epoch = engine.state.epoch
loss = engine.state.output['loss']
print ('Epoch {epoch}: train_loss = {loss}'.format(epoch=epoch, loss=loss))
accuracy = Accuracy(output_transform=lambda x: [x['y_pred'], x['y']])
accuracy.attach(trainer, 'acc')
trainer.run(data, max_epochs=10)
Note
A good practice is to use State also as a storage of user data created in update or handler functions.
For example, we would like to save new_attribute in the state:
def user_handler_function(engine):
engine.state.new_attribute = 12345
Resume training
Engine provides two methods to serialize and deserialize its internal state state_dict() and
load_state_dict(). In addition
with serializing model, optimizer, lr scheduler etc user can store the trainer and then resume the training from
an iteration. For example, using Checkpoint handler we can easily save checkpoints
containing serialized trainer, model, optimizer, etc
from ignite.engine import Engine, Events
from ignite.handlers import Checkpoint, DiskSaver
trainer = ...
model = ...
optimizer = ...
lr_scheduler = ...
data_loader = ...
to_save = {'trainer': trainer, 'model': model, 'optimizer': optimizer, 'lr_scheduler': lr_scheduler}
handler = Checkpoint(to_save, DiskSaver('/tmp/training', create_dir=True))
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.ITERATION_COMPLETED(every=1000), handler)
trainer.run(data_loader, max_epochs=100)
ls /tmp/training
> "checkpoint_50000.pth"
We can then restore the training from the last checkpoint.
from ignite.handlers import Checkpoint
trainer = ...
model = ...
optimizer = ...
lr_scheduler = ...
data_loader = ...
to_load = {'trainer': trainer, 'model': model, 'optimizer': optimizer, 'lr_scheduler': lr_scheduler}
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_file)
Checkpoint.load_objects(to_load=to_load, checkpoint=checkpoint)
trainer.run(train_loader, max_epochs=100)
Please, note that trainer can continue the training from the checkpoint iteration. In case when input data is torch.utils.data.DataLoader, previous batches are skipped and the first provided batch corresponds to the batch after the checkpoint iteration. Internally, while resuming, previous datapoint indices are just skipped without fetching the data.
Warning
However, while resuming from iteration, random data augmentations are not synchronized in the middle of the epoch and thus batches remaining until the end of en epoch can effectively be different of those from the initial run.
Complete examples that simulates a crash on a defined iteration and resumes the training from a checkpoint can be found here: